Supply: The School Investor
- Shared Blame: The coed mortgage disaster stems from rising school prices, insufficient authorities oversight, advanced reimbursement techniques, and debtors’ lack of monetary schooling.
- Disproportionate Affect: Low-income, first-generation, and minority college students face the best challenges in repaying loans, with defaults commonest amongst those that don’t full their levels.
Options: Addressing the disaster requires coverage reforms, simplifying mortgage applications, rising monetary literacy, and making certain school affordability by way of grant assist and managed tuition hikes.
The coed mortgage disaster is a fancy problem with a number of underlying causes. Rising school prices, elevated scholar borrowing, sophisticated reimbursement choices and an absence of satisfactory oversight have all contributed to the issue.
Accountability for this disaster is shared by a number of stakeholders:
- Federal and state governments
- Instructional establishments
- Scholar mortgage servicers
- Personal lenders
- Particular person debtors and their dad and mom (who could not totally grasp the long-term implications of their loans)
Faculties have raised tuition quicker than inflation, and authorities grants have didn’t hold tempo with will increase in school prices, pushing extra prices onto college students and their households. Mortgage servicers and lenders have additionally been criticized for deceptive practices, and lots of debtors lack entry to enough monetary schooling earlier than taking over debt.
Fixing the scholar mortgage downside requires a complete technique, not a single resolution. Addressing the issue would require a multifaceted strategy involving coverage reforms, simplifying the scholar mortgage applications, and higher regulation of school prices and lending practices. Moreover, rising monetary literacy might help college students make extra knowledgeable choices about borrowing and reimbursement.
In the end, understanding the foundation causes of the scholar mortgage disaster is vital to creating efficient and sustainable options.
The Scope Of The Scholar Mortgage Downside
Folks understand the expansion in scholar mortgage debt as an indication of an issue.
Listed below are the important thing scholar mortgage debt statistics as of the tip of final 12 months:
- Complete Scholar Mortgage Debt: $1.76 Trillion
- Quantity Of Scholar Mortgage Debtors: 43.2 Million Debtors
- Complete Federal Scholar Mortgage Debt: $1.60 Trillion
- Complete Personal Scholar Mortgage Debt: $130 Billion
- Common Federal Scholar Mortgage Debt Per Borrower: $37,088
- Median Federal Scholar Mortgage Debt Per Borrower: $19,281
Scholar loans are the second-largest class of family debt, second solely to mortgage debt. Scholar mortgage debt exceeds excellent auto loans and bank card debt.
Most school graduates begin their careers saddled with tens of 1000’s of {dollars} in debt, which may take a decade or longer to repay. The monetary burden of scholar loans can delay main milestones like shopping for a house, beginning a household, or saving for retirement.
The basis of the problem will not be the existence of scholar loans themselves, however slightly a school completion downside. The overwhelming majority of school graduates are capable of repay their scholar loans.
Undergraduate college students who go away college with out ending a level are 4 occasions extra more likely to default on their loans than those that graduate. Actually, three-quarters of all defaults are from debtors who dropped out and didn’t earn a level, leaving them with debt however not the credentials wanted to spice up their earnings and repay it.
Default charges stay stubbornly excessive, even with income-driven reimbursement plans, as many debtors have hassle understanding and navigating the reimbursement plans.
Nonetheless, scholar mortgage debt is much less widespread than different types of debt. Solely 21.7% of households have scholar mortgage debt, whereas 45.2% carry bank card balances, 40.9% have mortgages, and 34.7% owe on auto loans.
Lately, new scholar mortgage borrowing has declined, with whole annual federal scholar mortgage debt dropping from its peak of $106 billion in 2011-2012 to lower than $80 billion per 12 months. This pattern is partly as a consequence of fewer debtors and a decline within the common mortgage quantity for many kinds of loans, aside from PLUS loans.
Nonetheless, the full scholar mortgage stability continues to develop, as new loans are taken out every year whereas previous loans are repaid slowly over a long time.
Associated: Discover extra scholar mortgage debt statistics right here.

Supply: The School Investor
Affect Of Scholar Mortgage Debt
Regardless of issues in regards to the broader financial impression of scholar mortgage debt, annual scholar mortgage funds symbolize a small fraction of the U.S. GDP. Nevertheless, the burden on particular person debtors could be substantial, as scholar mortgage funds typically take priority over different monetary priorities, like paying off shopper debt or constructing financial savings. Though the everyday scholar mortgage cost is decrease than a typical automotive cost, it may possibly nonetheless pressure the funds of many households.
The impression of scholar mortgage debt shouldn’t be uniform throughout all demographics. Low-income, first-generation school college students, impartial college students, and debtors who’re Black, Hispanic or Native American usually tend to borrow bigger quantities and face higher issue repaying their loans. Feminine graduates are additionally extra more likely to have scholar mortgage debt and sometimes earn much less after commencement, making reimbursement more difficult.
When a borrower struggles to repay their scholar loans, the scholar mortgage debt could persist into previous age, with senior residents way more more likely to be in default than youthful debtors. Based on the Authorities Accountability Workplace (GAO), 37% of debtors aged 65 and older and 54% of these aged 75 and older are in default. The federal authorities may even garnish Social Safety advantages to repay defaulted loans, which is especially harsh for seniors who depend on these funds for necessities like meals and medication. This apply is each financially dangerous and ethically questionable.
In the end, the burden of scholar mortgage debt will increase monetary stress and might hurt debtors’ productiveness and general well-being. Addressing the scholar mortgage problem requires a nuanced strategy, specializing in school completion, improved mortgage servicing, higher monetary schooling, and focused coverage reforms to alleviate the pressure on essentially the most susceptible debtors.
Right here’s a breakdown of who bears accountability for the scholar mortgage downside.
The Federal Authorities
Over 92% of all scholar loans are federal, making the U.S. authorities the dominant participant within the scholar mortgage market and a central contributor to the present debt disaster. Whereas the federal mortgage system was designed to make increased schooling extra accessible, it has additionally led to a major improve in scholar debt, with unintended and damaging penalties for a lot of debtors.
Federal scholar loans have a number of traits that resemble predatory lending practices. These embrace granting loans with out satisfactory evaluation of a borrower’s potential to repay, excessive rates of interest and costs, curiosity capitalization, adverse amortization, and insufficient disclosures.
For instance, not like personal lenders, the federal authorities doesn’t consider the borrower’s debt-to-income ratio or potential future earnings. This makes it straightforward for college kids to borrow giant sums, typically past what they’ll fairly anticipate to repay after commencement.
Federal scholar loans lack many customary shopper protections that apply to different kinds of loans. For example:
- No Statute of Limitations: Federal scholar loans don’t expire, which means the debt can comply with debtors for all times.
- No Protection of Infancy: Even debtors who took out loans as minors can’t discharge their debt based mostly on age.
- Aggressive Assortment Powers: The federal authorities has highly effective instruments for debt assortment, reminiscent of garnishing wages, seizing tax refunds, and even withholding Social Safety incapacity and retirement profit funds. These measures could be devastating, particularly for older debtors who rely on these advantages for fundamental wants like meals and drugs.
- Excessive Assortment Fees: When a borrower defaults, as a lot as a fifth of the scholar mortgage cost is siphoned off to cowl assortment costs earlier than the remainder is utilized to curiosity and the scholar mortgage stability. This slows the reimbursement trajectory significantly, sustaining a excessive stage of debt.
The Mum or dad PLUS Mortgage and Grad PLUS Mortgage applications permit for just about limitless borrowing, with the one restriction being the full value of attendance minus different monetary assist. The credit score checks for these loans are minimal, contemplating solely previous credit score points with out assessing future reimbursement potential.
“This creates a moral hazard for students and colleges, enabling families to borrow freely without facing immediate consequences, which in turn drives up the amount of debt.”
Federal scholar mortgage reimbursement plans are notoriously advanced. Whereas income-driven reimbursement (IDR) choices are designed to make scholar loans extra reasonably priced by basing month-to-month funds on the borrower’s earnings slightly than the quantity owed, they’re typically complicated and tough to navigate.
Many debtors wrestle to pick out the most effective reimbursement plan for his or her state of affairs, lacking out on alternatives to decrease their funds, scale back curiosity, or qualify for mortgage forgiveness. The complexity of the system contributes to missed funds, mortgage delinquency, and defaults.
For instance, over 40% of debtors are enrolled within the Normal reimbursement plan, which can value them greater than an income-driven reimbursement plan.

Supply: The School Investor
In IDR plans, debtors could discover that their month-to-month funds are lower than the accruing curiosity, inflicting the full mortgage stability to extend — a phenomenon often known as adverse amortization. Whereas remaining debt could also be forgiven after 20 or 25 years, the system primarily gives a retroactive grant for over-borrowing, creating long-term monetary instability for a lot of.
Policymakers have prioritized scholar loans over grants as a strategy to pay for increased schooling as a result of loans are cheaper to the federal government within the brief time period. Authorities grants have didn’t hold tempo with will increase in school prices, shifting extra of the burden of paying for school to college students and their households.
Scholar loans are the one type of monetary assist (for those who name it that) that demonstrates any diploma of elasticity, inflicting debt at commencement to develop quicker than inflation.
Trending Article Proper Now
30 Most Costly Faculties
- The costliest faculties in the USA all value over $65,000 per 12 months in simply tuition.
- Once you think about room and board, together with different bills, you could possibly pay upwards of $90,000 per 12 months.
Faculties And Universities
School prices have skyrocketed, far outpacing inflation and wage development. Faculties have continued to extend tuition, understanding that college students have entry to federal loans to cowl rising prices.
Tuition and costs at private and non-private non-profit 4-year faculties have elevated greater than 20-fold over the previous 50 years. Even after adjusting for inflation, school prices have greater than tripled, placing increased schooling more and more out of attain for a lot of households.
One main issue driving tuition hikes is the feast-famine cycle of state funding for public faculties and universities. When states face finances shortfalls, they typically scale back funding for increased schooling, forcing public faculties to compensate by elevating tuition and costs.
This shifts extra of the monetary burden onto college students and households, resulting in a surge in scholar borrowing. Because of this, college students are more and more reliant on federal loans to bridge the hole between the price of attendance and their potential to pay.
Along with rising prices, some faculties aggressively market their applications to low-income and susceptible populations, making guarantees of high-paying jobs that usually fail to materialize. These college students, lured in by the prospect of upward mobility, ceaselessly find yourself with substantial debt however no diploma. With out the elevated incomes potential {that a} school diploma sometimes gives, they wrestle to repay their loans, making them more likely to default.
College students who borrow closely however don’t full their levels are at significantly excessive threat. They face bigger money owed relative to the worth of their schooling, resulting in monetary pressure and elevated probability of default. For a lot of debtors, this will develop into a lifelong monetary burden, affecting their potential to purchase a house, begin a household, or save for retirement.
Debtors (And Their Mother and father)
Many college students depend on scholar loans to cowl tuition, charges, and residing bills. Nevertheless, some borrow greater than what they should pay the school payments, treating scholar loans as if they’re free cash. However, scholar loans should be repaid, normally with curiosity.
The complexity of the system can also be an issue, as a result of debtors do not perceive how a lot they owe or easy methods to monitor their mortgage balances.
This confusion typically leads to underestimating the full debt and the price of reimbursement. The dearth of transparency and clear communication can go away debtors overwhelmed and ill-prepared to handle their debt.
Some school college students borrow greater than they’ll realistically afford to repay, fueled by unrealistic expectations about their future earnings. They assume {that a} school diploma will routinely result in high-paying jobs, however this isn’t all the time the case.
This overconfidence can result in monetary misery, particularly if their precise post-graduation earnings are decrease than anticipated. Moreover, there’s a rising component of ethical hazard, the place some debtors imagine that their loans could finally be forgiven or that they won’t be held totally accountable for repaying the debt.
Many debtors select reimbursement plans that stretch the time period of the mortgage, choosing decrease month-to-month funds with out totally understanding the implications. Whereas an extended reimbursement time period could scale back the month-to-month scholar mortgage cost, offering short-term aid, it considerably will increase the full curiosity paid over the lifetime of the mortgage. In lots of instances, debtors find yourself paying way over the unique quantity borrowed, extending their monetary burden for years and even a long time.
Some of the important points is the shortage of monetary literacy amongst school college students. Many don’t totally grasp the phrases of their loans or the long-term impression of taking over important debt to pay for school.
Monetary counseling, if offered in any respect, is usually inadequate or poorly timed. This lack of schooling can result in overborrowing and difficulties in managing debt, setting college students up for monetary pressure after commencement.
Mortgage Servicers
Mortgage servicers additionally contribute to the issue by missing transparency of their recommendation to debtors. In contrast to fiduciaries, mortgage servicers should not required to prioritize the choices which might be within the borrower’s greatest pursuits, and this has led to widespread criticism.
Mortgage servicers have been criticized for offering inaccurate or deceptive info, which complicates the already complicated reimbursement course of. As a substitute of providing choices that might scale back the borrower’s long-term debt burden, servicers typically fail to supply clear explanations of reimbursement plans and their eligibility necessities. Many debtors report difficulties enrolling in income-driven reimbursement (IDR) plans, actually because they obtain conflicting recommendation or encounter bureaucratic hurdles.
For instance, we performed a survey of scholar mortgage debtors and solely about two-thirds have been capable of perceive their scholar mortgage reimbursement plan choices:
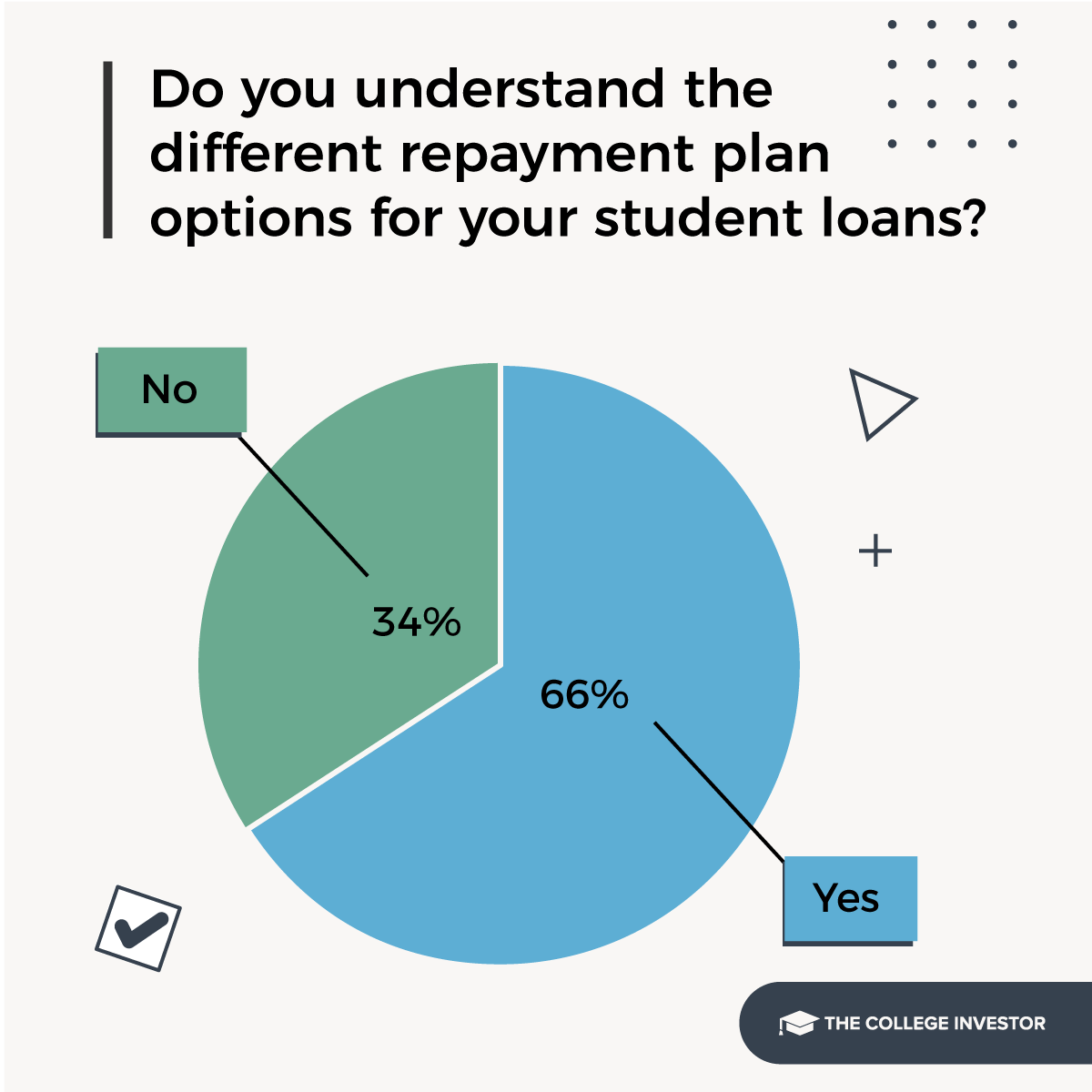
Supply: The School Investor
Mortgage servicers have been accused of steering debtors to forbearance as an alternative of income-driven reimbursement plans. A forbearance permits the borrower to quickly pause funds. Nevertheless, unpaid curiosity continues to accrue, inflicting the mortgage stability to develop. Debtors are left with the next mortgage stability than they began with, digging them right into a deeper gap.
Options To The Scholar Mortgage Downside
There are a number of options that may scale back reliance on scholar mortgage debt and make scholar loans simpler to repay.
Increase Grant Help For Low-Earnings College students
The federal authorities ought to change loans with grants within the monetary assist packages of financially susceptible college students, reminiscent of low-income college students and present/former foster youth.
A major improve within the Pell Grant, probably doubling or tripling the present common quantity, can be a crucial first step. This improve ought to be carried out instantly and listed to inflation to take care of its worth over time.
Eligibility ought to be tied to college students from households incomes as much as 150% of the federal poverty line, making certain focused assist with out increasing eligibility unnecessarily.
Simplify The Federal Scholar Mortgage System
The present system is overly advanced, with a number of kinds of loans and reimbursement plans, making it tough for debtors to make knowledgeable decisions.
Consolidating the choices into two principal reimbursement plans would streamline the method: customary reimbursement (stage funds with a 10-year time period) and income-based reimbursement (10% of the surplus of earnings over 150% of the poverty line, with the remaining debt forgiven after 20 years of funds).
Earnings-based reimbursement is meant to supply a security internet for debtors whose debt exceeds their earnings.
Implement Wise Mortgage Limits
Scholar mortgage borrowing limits ought to be set based mostly on the borrower’s future incomes potential, slightly than the price of attendance alone.
Combination borrowing ought to be capped at not more than the anticipated annual post-graduation earnings, making certain that debtors can fairly anticipate to repay their loans inside a decade. This may assist forestall over-borrowing and scale back default threat.
Annual mortgage limits ought to be derived from the combination limits.
Get rid of the PLUS Mortgage Program
The PLUS mortgage program for fogeys and graduate college students permits borrowing past affordable limits, typically resulting in extreme debt burdens. Eliminating this program and adjusting rates of interest on the Federal Direct Stafford Mortgage to take care of income neutrality would assist include borrowing and focus sources on need-based assist.
Improve Monetary Literacy Schooling
Requiring complete monetary literacy coaching earlier than college students take out loans might help guarantee they perceive the long-term impression of borrowing. Personalised counseling ought to be offered, tailor-made to every scholar’s monetary state of affairs and profession plans.
Common, standardized month-to-month statements must also be despatched throughout school, conserving debtors knowledgeable about their mortgage standing and the expansion of their debt. Growing consciousness of the impression of scholar mortgage debt will assist debtors train restraint.
Standardize Mortgage Disclosures
Federal scholar loans ought to undertake the identical disclosure requirements as personal loans, providing uniform transparency.
This would supply debtors with a clearer understanding of the phrases, dangers, and potential prices related to their loans, whatever the lender.
Focused Mortgage Forgiveness
Scholar mortgage forgiveness ought to be focused and needs-based, specializing in debtors who’re actually unable to repay their debt. Precedence ought to be given to:
- Low-income debtors fighting reimbursement.
- Senior Residents, significantly these whose Social Safety advantages are liable to garnishment.
- Debtors in important however low-paying professions, reminiscent of public service or educating in underserved areas.
Enhance School Completion Charges
A key think about scholar mortgage default is the failure to achieve the end line. College students who don’t graduate are considerably extra more likely to wrestle with mortgage reimbursement.
Insurance policies that concentrate on rising school retention and completion charges, reminiscent of enhanced educational help and advising, might help extra college students earn a level and enhance their potential to repay loans.
Do not Miss These Different Tales:

