
SpaceX
The Federal Aviation Administration authorised the industrial launch license for the fourth take a look at flight of SpaceX’s Starship rocket Tuesday, with liftoff from South Texas focused for simply after dawn Thursday.
“The FAA has authorised a license authorization for SpaceX Starship Flight 4,” the company stated in an announcement. “SpaceX met all security and different licensing necessities for this take a look at flight.”
Shortly after the FAA introduced the launch license, SpaceX confirmed plans to launch the fourth take a look at flight of the world’s largest rocket at 7:00 am CDT (12:00 UTC) Thursday. The launch window runs for 2 hours.
This flight follows three prior demonstration missions, every progressively extra profitable, of SpaceX’s privately-developed mega-rocket. The final time Starship flew—on March 14—it accomplished an eight-and-a-half minute climb into house, however the ship was unable to maneuver itself because it coasted almost 150 miles (250 km) above Earth. This controllability downside brought about the rocket to interrupt aside throughout reentry.
On Thursday’s flight, SpaceX officers will anticipate the ascent portion of the take a look at flight to be equally profitable because the launch in March. The targets this time can be to display Starship’s capacity to outlive probably the most excessive heating of reentry, when temperatures peak at 2,600° Fahrenheit (1,430° Celsius) because the automobile plunges into the ambiance at greater than 20 instances the pace of sound.
SpaceX officers additionally hope to see the Tremendous Heavy booster information itself towards a tender splashdown within the Gulf of Mexico simply offshore from the corporate’s launch website, generally known as Starbase, in Cameron County, Texas.
“The fourth flight take a look at turns our focus from attaining orbit to demonstrating the flexibility to return and reuse Starship and Tremendous Heavy,” SpaceX wrote in an summary of the mission.
Final month, SpaceX accomplished a “moist gown rehearsal” at Starbase, the place the launch staff absolutely loaded the rocket with cryogenic methane and liquid oxygen propellants. Earlier than the follow countdown, SpaceX test-fired the booster and ship on the launch website. Extra just lately, technicians put in parts of the rocket’s self-destruct system, which might activate to explode the rocket if it flies off beam.
Then, on Tuesday, SpaceX lowered the Starship higher stage from the highest of the Tremendous Heavy booster, presumably to carry out closing touch-ups to ship’s warmth protect, comprised of 18,000 hexagonal ceramic tiles to guard its stainless-steel construction throughout reentry. Floor groups have been anticipated to lift the ship, or higher stage, again on prime of the booster a while Wednesday, returning the rocket to its full top of 397 ft (121 meters) forward of Thursday morning’s launch window.
The tick-tock of Starship’s fourth flight
If all goes in line with plan, SpaceX’s launch staff will begin loading 10 million kilos of super-cold propellants into the rocket round 49 minutes earlier than liftoff Thursday. The methane and liquid oxygen will first circulation into the smaller tanks on the ship, then into the bigger tanks on the booster.
The rocket ought to be absolutely loaded about three minutes previous to launch, and following a sequence of automated checks, the pc controlling the countdown will give the command to mild the booster’s 33 Raptor engines. Three seconds later, the rocket will start its vertical climb off the launch mount, with its engines able to producing greater than 16 million kilos of thrust at full energy.
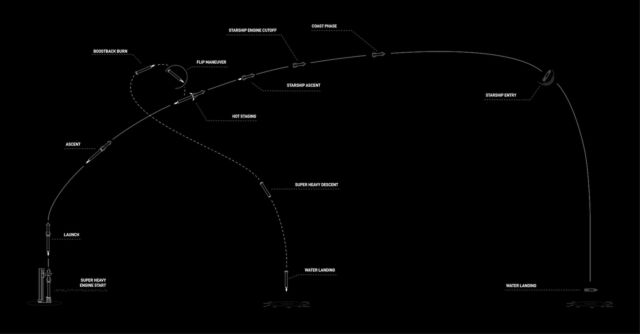
Heading east from the Texas Gulf Coast, the rocket will exceed the pace of sound in a couple of minute, then start shutting down its 33 principal engines round 2 minutes and 41 seconds after liftoff. Then, simply because the Tremendous Heavy booster jettisons to start a descent again to Earth, Starship’s six Raptor engines will ignite to proceed pushing the higher portion of the rocket into house. Starship’s engines are anticipated to burn till T+plus 8 minutes, 23 seconds, accelerating the rocket to close orbital velocity with sufficient vitality to fly an arcing trajectory midway all over the world to the Indian Ocean.
All of this can be just like the occasions of the final Starship launch in March. What differs within the flight plan this time entails the makes an attempt to steer the booster and ship again to Earth. That is necessary to put the groundwork for future flights, when SpaceX desires to deliver the Tremendous Heavy booster—the dimensions of the fuselage of a Boeing 747 jumbo jet—to a touchdown again at its launch pad. Ultimately, SpaceX additionally intends to recuperate reusable Starships again at Starbase or different spaceports.
SpaceX
Based mostly on the outcomes of the March take a look at flight, SpaceX nonetheless has so much to show in these areas. On that flight, the engines on the Tremendous Heavy booster couldn’t full all of the burns required to information the rocket towards the splashdown zone within the Gulf of Mexico. The booster misplaced management because it plummeted towards the ocean.
Engineers traced the failure to blockage in a filter the place liquid oxygen flows into the Raptor engines. Notably, the same downside occurred on the second Starship take a look at flight final November. The Tremendous Heavy booster awaiting launch Thursday has extra {hardware} to enhance propellant filtration capabilities, in line with SpaceX. The corporate additionally carried out “operational modifications” on the booster for the upcoming take a look at flight, together with jettison of the Tremendous Heavy’s staging ring, which sits between the booster and ship throughout launch, to scale back the rocket’s mass throughout descent.
SpaceX has lots of expertise bringing again its fleet of Falcon 9 boosters. The corporate now boasts a streak of greater than 240 profitable rocket landings in a row, so it is cheap to anticipate SpaceX will overcome the problem of recovering the bigger Tremendous Heavy booster.
The thorny situation of tiles
Starship, nonetheless, is a unique animal. Regardless of having fewer engines, SpaceX’s ambitions for the ship require it to be immensely extra advanced than the booster. In the end, these objectives for Starship embrace satellite tv for pc deployments, interplanetary transport, landings on the Moon and Mars, and refueling in orbit. However first, SpaceX should present that Starship can reliably journey between Earth’s floor and low-Earth orbit.
On Flight 3 in March, the Starship higher stage misplaced the flexibility to regulate its orientation after turning off its principal engines upon reaching house. SpaceX stated engineers decided this was because of clogged valves utilized by response management thrusters on the higher stage, and the corporate stated it’s including extra roll management thrusters on upcoming Starships.
The roll management downside prevented SpaceX from attaining two take a look at targets on the final Starship take a look at flight. One was an try and reignite one of many ship’s Raptor engines in house, a functionality that SpaceX should routinely use on future Starship flights. The opposite was the managed reentry of the 165-foot-long (50-meter) higher stage. With out absolutely functioning thrusters, the ship fell again into the ambiance within the incorrect perspective, and SpaceX misplaced contact with the automobile because of extra heating.
This time, SpaceX will attempt to hold it easy. In fact, easy is a relative time period in terms of spaceflight and Starship. On Flight 4, there is no deliberate restart of a Raptor engine whereas the ship is in house. The shortage of such a take a look at on this flight means the subsequent launch—Flight 5—will possible goal the same suborbital trajectory, somewhat than going all the way in which into orbit. Presumably, SpaceX, and maybe federal regulators, would first wish to see Starship show it may well execute a braking burn to return to Earth, somewhat than placing the automobile into orbit and having it reenter the ambiance unguided if the engine begin failed.
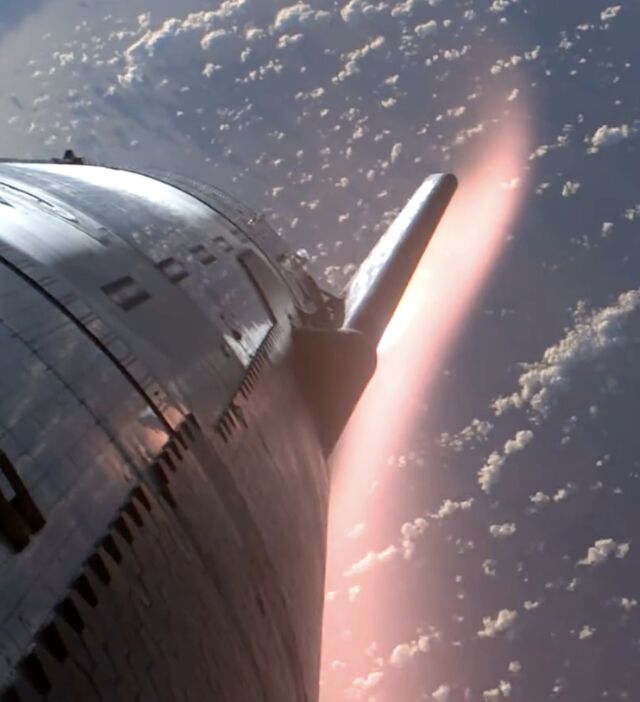
This automobile additionally does not have a payload bay door just like the final Starship opened and closed in house. As a substitute, the ship will drift by means of house till its flight path brings it again into the higher ambiance round 47 minutes into the flight.

SpaceX
That is when the ceramic tiles that make up Starship’s warmth protect will get to work. The tiles, every in regards to the measurement of a dinner plate, are related in operate to these used on NASA’s house shuttle, in that they insulate the ship’s main construction from the blistering warmth of reentry.
Elon Musk, SpaceX’s founder and CEO, wrote on X final week that gathering information on the tiles’ efficiency in flight is significant.
“It is a matter of execution, somewhat than concepts,” he wrote. “Until we make the warmth protect comparatively heavy, as is the case with our Dragon capsule, the place reliability is paramount, we are going to solely uncover the weak factors by flying.”
To be able to make actual Musk’s lofty ambitions for a completely and quickly reusable rocket, Starship’s warmth protect should be resilient and require little in the way in which of refurbishment between flights. SpaceX has a protracted option to go there.
“Proper now, we aren’t resilient to lack of a single tile in most locations, because the secondary containment materials will most likely not survive,” Musk wrote. “It is a thorny situation certainly, on condition that huge assets have been utilized to resolve it, up to now to no avail.”
If it survives the warmth of reentry, Starship will descend into the decrease ambiance stomach first and decelerate to subsonic pace below the management of aerodynamic flaps, just like miniature wings. Lastly, the ship will reignite a subset of its Raptor engines—most likely two—and rapidly flip from horizontal to vertical to settle into the waters of the Indian Ocean between Madagascar and Australia. If this occurs, cue the champagne.
Regulatory waivers
The FAA additionally made some modifications with the launch license for SpaceX’s fourth Starship take a look at flight that might pace up the method of issuing licenses for future launches.
With the primary three Starship launches, the FAA license required SpaceX conduct a mishap investigation with federal oversight if the rocket failed to succeed in its vacation spot intact. The result of the final take a look at flight—Starship’s breakup over the Indian Ocean—triggered such an investigation by SpaceX.
The FAA is charged with guaranteeing public security throughout industrial house launches and reentries. In a Starship mishap investigation, the company’s function is to supervise the inquiry and settle for the outcomes of SpaceX’s investigation earlier than issuing a license for the subsequent launch.
However this strategy is not congruent with SpaceX’s roadmap for Starship growth. SpaceX’s iterative strategy is rooted in take a look at flights, the place engineers be taught what and what does not work, then attempt to rapidly repair it and fly once more. A crash, or two or three, is all the time attainable, if not going. The FAA is making an adjustment for this week’s mission.
“As a part of its request for license modification, SpaceX proposed three situations involving the Starship entry that may not require an investigation within the occasion of the lack of the automobile,” the FAA stated in an announcement.
Based mostly on language within the code of federal rules, the FAA has the choice to approve these exceptions. The FAA accepted three attainable outcomes for the upcoming Starship take a look at flight that may not set off what would possible be a months-long mishap investigation.
These exceptions embrace the failure of Starship’s warmth protect throughout reentry, if the ship’s flap system is unable to supply enough management below excessive dynamic stress, and the failure of the Raptor engine system through the touchdown burn. If considered one of these situations happens, the FAA won’t require a mishap investigation, offered there was no severe harm or fatality to anybody on the bottom, no harm to unrelated property, and no particles exterior designated hazard areas.
This variation is kind of vital for the FAA and SpaceX. It exhibits that federal regulators, affected by staffing and funding shortages, are making strikes to try to sustain with SpaceX’s speedy, and sometimes ever-changing, growth of Starship.
“If a unique anomaly happens with the Starship automobile, an investigation could also be warranted, in addition to if an anomaly happens with the Tremendous Heavy booster rocket,” the FAA stated.

