It reduces Social Safety functions and new beneficiaries.
Enthusiasm appears to be working excessive for Household and Medical Depart applications. My views are combined: as a human I can see some profit; as an individual making an attempt to run a small group, prolonged leaves are simply annoying.
Some critics have a extra particular concern – particularly, that Momentary Incapacity Insurance coverage (TDI), which is often included in these applications, might function an on-ramp to Social Safety’s Incapacity Insurance coverage (DI) program. Since TDI advantages aren’t thought of earnings, they may present wanted funds in the course of the prolonged utility course of, encouraging staff to use, and finally rising the DI rolls.
In distinction, lovers of a nationwide paid depart program argue that TDI would permit staff – notably older staff who’re most in danger – to regulate to well being shocks and resume employment, decreasing reliance on DI.
In a current examine, my colleagues tried to kind out the proof. They started with a pattern of full-time staff ages 50-60 who expertise a brand new work-limiting shock and tracked these staff for 2 to 4 years, permitting them ample time to submit a DI utility. They broke the pattern into two teams: 1) these with a persistent and extreme incapacity who had been potential DI candidates; and a pair of) these with much less extreme impairments who’re unlikely to qualify for DI.
And so they took benefit of the truth that staff can entry TDI provided that they reside in states with TDI mandates or if their employer voluntarily provides these advantages. Since information on employer protection is proscribed, they in contrast staff residing in states with longstanding TDI mandates – California, New Jersey, New York, and Rhode Island – with related staff in different states.
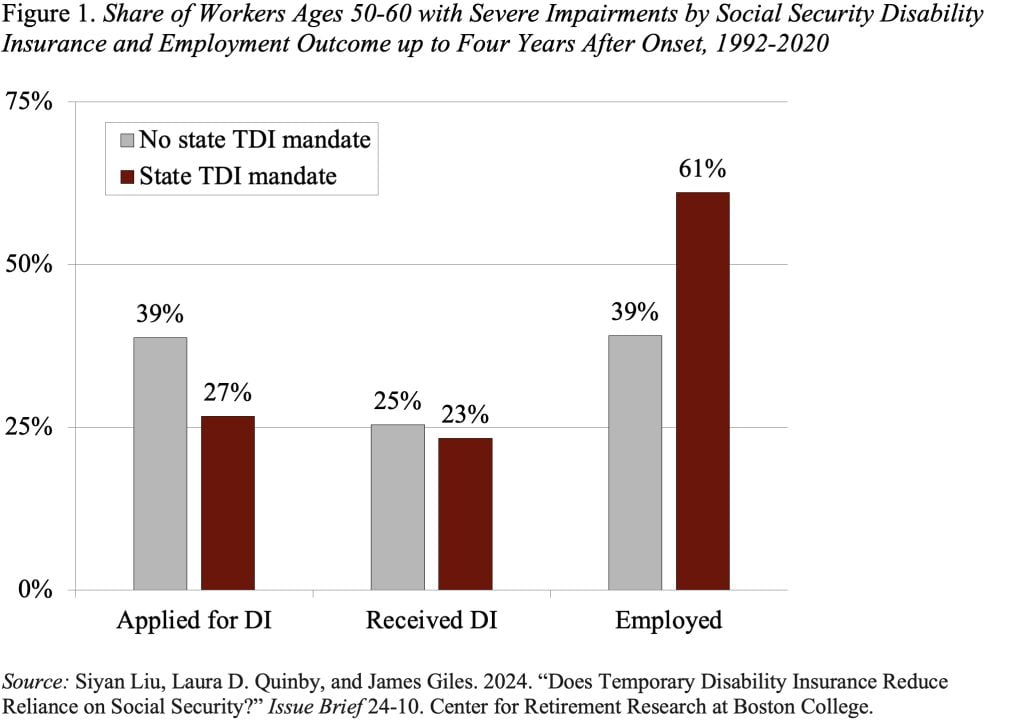
Influence of TDI for These with Extreme Disabilities
As much as 4 years after incapacity onset, 39 % of potential DI candidates had submitted a declare for DI in non-mandate states, in comparison with solely 27 % in states with a TDI mandate (see Determine 1). This drop in functions, nonetheless, produces solely a small decline in precise profit receipt – suggesting that almost all of these not making use of would seemingly not have certified. By way of employment – as much as 4 years later, solely 39 % of potential DI candidates are employed in non-mandate states, in comparison with 61 % in states with a TDI mandate. These findings appear to substantiate that the drop in functions not solely alleviates the executive burden for the Social Safety Administration, but in addition permits would-be candidates to proceed working.
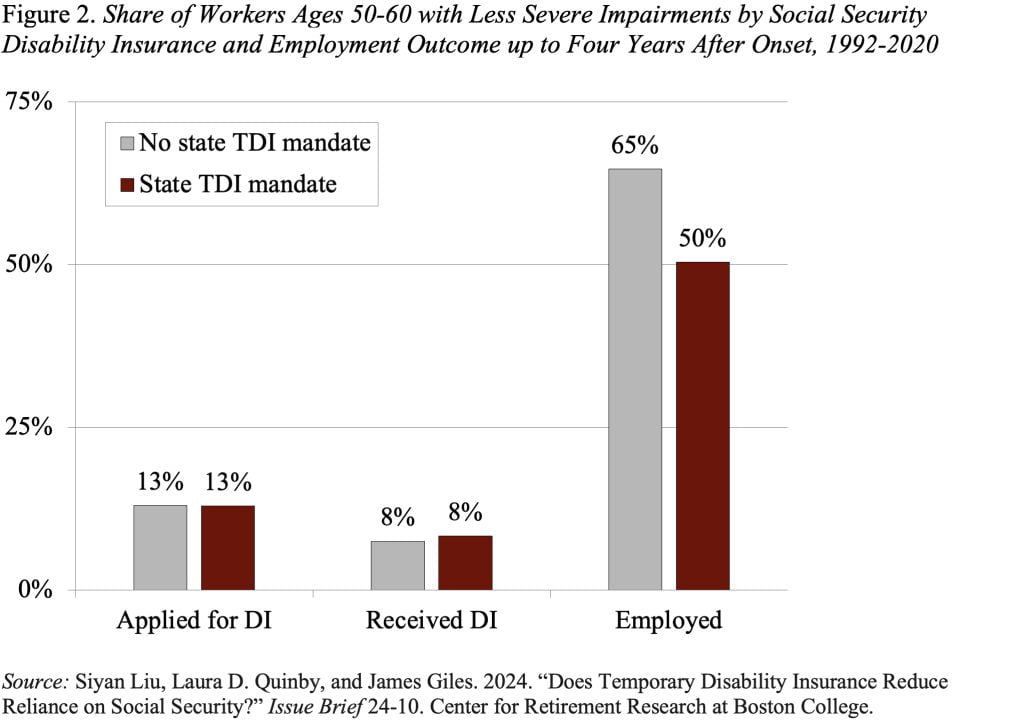
Influence of TDI for Staff with Much less Extreme Impairments
As anticipated, entry to TDI has no affect on the share of staff with much less extreme impairments who apply for or obtain DI (see Determine 2). Nevertheless, TDI does appear to cut back employment. Whereas the employment fee was 65 % in non-mandate states – as much as 4 years after incapacity onset – it was solely 50 % in states with a TDI mandate.
This examine ought to relieve considerations that increasing TDI will adversely have an effect on Social Safety DI. For these with extreme disabilities, TDI seems to cut back the DI utility fee rather a lot, the incapacity rolls just a little, and improve employment as much as 4 years after a well being shock. For these with much less extreme situations, TDI has no affect on DI functions or acceptances. The one considerably worrying result’s that TDI appears to result in earlier retirement for these with much less extreme impairments.

