Within the early Eighties, places of work had been noisy locations, stuffed with the sound of metallic placing inked ribbons to mark characters on paper. IBM Selectric typewriters clacked, daisy wheel printers clattered, and dot-matrix printers made loud ripping sounds.
At present, these noises are gone. And although we do spend extra time studying on screens, we haven’t stopped printing on paper.
The principle cause for the quiet? The inkjet printer. Whereas laser printers do the massive printing jobs in industrial settings, the inkjet printer has develop into
the printer most of us use at house and on the workplace.
The printhead of an inkjet printer performs a exceptional process. Even on the coarse decision of 96 dots per inch (dpi), as was typical for the primary fashions within the Eighties, the space from dot heart to dot heart is a mere 260 micrometers. To fill an ordinary letter web page that has 2.5-centimeter margins would require greater than half 1,000,000 particular person ink droplets. Supply of these tiny droplets includes transferring them with very exact management, repeated an enormous variety of occasions as quickly as potential. This course of is ideally suited to microelectromechanical programs (MEMS), that are digital units with microscopic elements that make use of motion.
If there’s a method to bundle one thing in microscopic droplets with the suitable fluid properties, likelihood is somebody is trying to adapt inkjet know-how to work with it.
As with all microtechnology, the specs of inkjet programs have advanced significantly over time. A typical inkjet printhead within the mid-Eighties had 12 nozzles working in parallel, every one emitting as much as 1,350 droplets per second, to print 150 alphanumeric characters per second. At present, a high-end inkjet printhead utilized in a industrial printing press could comprise 21,000 nozzles, every nozzle printing 20,000 to 150,000 dots per second. Every drop of ink could also be simply 1.5 picoliters—a picoliter is one-trillionth of a liter—and measure roughly 14 micrometers in diameter.
Surpassing the visions of its creators, the inkjet know-how utilized in these printers has discovered a number of functions past placing dots on paper. These embody making DNA microarrays for genomics, creating electrical traces for printed circuit boards, and constructing 3D-printed constructions. Future makes use of might embody personalised medication and improvement of superior batteries.
Certainly, a seek for patents containing the phrase “inkjet” at this time returns greater than 92,000 outcomes. If there’s a method to bundle one thing in microscopic droplets with the suitable fluid properties, likelihood is somebody is trying to adapt inkjet know-how to work with it.
How MEMS Reworked Inkjet Printing
Inkjet know-how dates again to 1948, when Swedish inventor
Rune Elmqvist patented a chart recorder whereby a really skinny glass tube emitting a steady jet of ink was steered to make a hint on a transferring strip of paper. A few years later, he demonstrated his invention within the type of a tool for recording electrocardiograms.
In 1965, Richard G. Candy of Stanford College
developed a chart recorder during which the jet of ink was damaged right into a uniform stream of electrically charged droplets. Diverter electrodes on both facet of the stream might allow the drops to proceed straight to the paper, or else deflect them onto an absorbent pad or right into a gutter to be collected and reused.
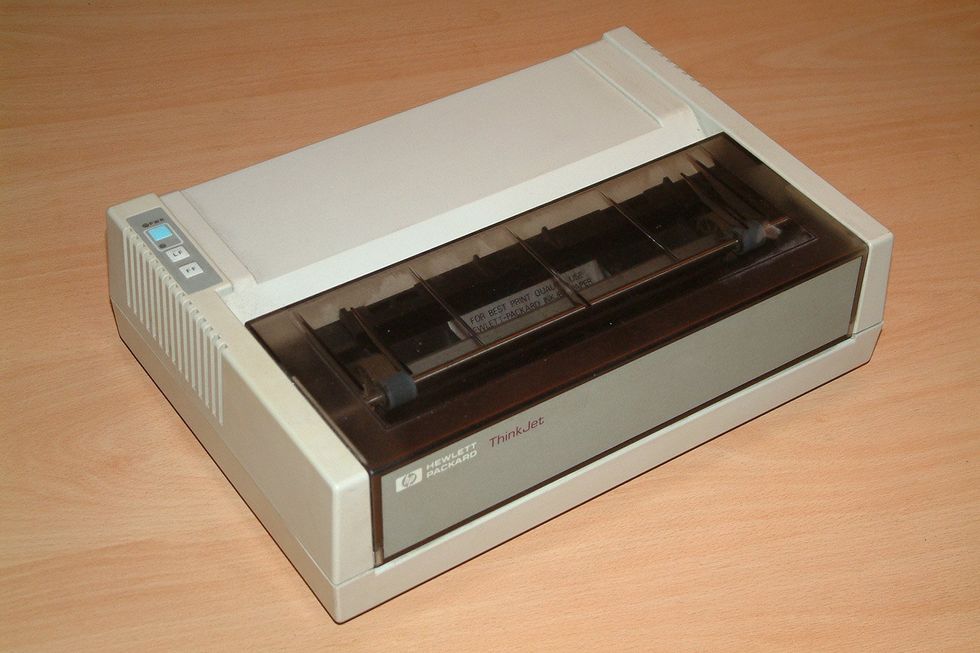

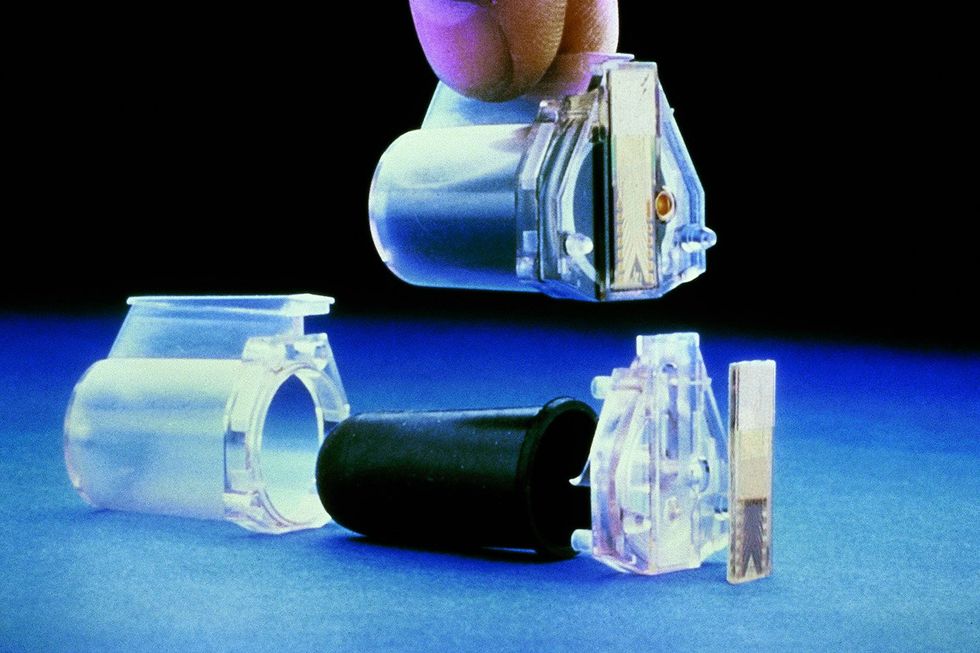 In April 1984, the HP ThinkJet [top] ushered within the period of desktop inkjet printing. The Thinkjet’s ink cartridge [bottom] delivered hundreds of microscopic droplets a second from 12 nozzles. The MEMS know-how to carry out that feat was completely throughout the printhead.HP
In April 1984, the HP ThinkJet [top] ushered within the period of desktop inkjet printing. The Thinkjet’s ink cartridge [bottom] delivered hundreds of microscopic droplets a second from 12 nozzles. The MEMS know-how to carry out that feat was completely throughout the printhead.HP
This know-how known as steady inkjet printing, and by 1976 IBM had integrated it in a industrial printer, the
IBM 6640. However steady inkjets lose ink to evaporation even when recycling is used, limiting their enchantment.
To get across the wastefulness of steady inkjets, others labored on growing drop-on-demand inkjet printers, the place every orifice on the printhead emits one drop of ink at a time, avoiding the waste of a continuous stream of drops. Floor stress holds the ink in place in a tiny open nozzle till a mechanism pushes the ink to eject a drop. Every drop hitting the paper creates a dot, and transferring the printhead forwards and backwards builds up a picture. A printhead with a number of orifices can emit many drops of ink concurrently, so every go of the printhead throughout the web page provides a strip of the picture, not only a single drop-thin line.
Within the late Seventies, Siemens was the primary to promote a drop-on-demand inkjet printer. It got here not as a stand-alone gadget like a contemporary desktop printer, however as an integral a part of a pc terminal, the
Siemens PT80i (Printer Terminal 80 Inkjet). The printer used piezoelectric actuators surrounding 12 ink tubes, which fed 12 nozzles to shoot ink droplets, printing 270 characters per second.
Piezoelectric units depend on how some supplies, resembling ceramic lead-zirconate-titanate (PZT), change form when subjected to a voltage. This impact has proved extraordinarily helpful in MEMS normally, for producing exact forces and movement on command. If a layer of PZT is bonded to a nonpiezoelectric materials, forming what’s known as a bimorph, it should bend when uncovered to a voltage. Within the piezoelectric inkjet nozzle, the bending of the bimorph pushes ink out of the orifice. [For another application of piezoelectric MEMS technology, see “How Ultrasound Became Ultra Small.”]
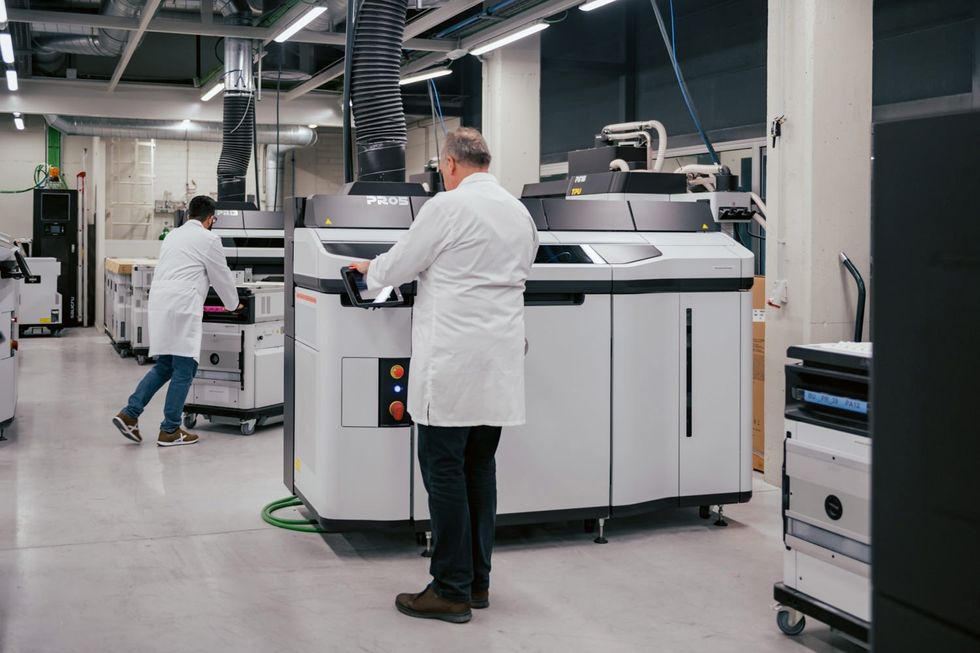 The HP Jet Fusion 5200 industrial 3D printer makes use of an inkjet course of to construct elements out of nylon, polypropylene, or polyurethane.HP
The HP Jet Fusion 5200 industrial 3D printer makes use of an inkjet course of to construct elements out of nylon, polypropylene, or polyurethane.HP
This novel printing know-how, nonetheless, was not but as reliable as confirmed impression printers within the Seventies, and the entire Siemens terminal turned unusable if the printer failed, so it didn’t catch on.
In the meantime, researchers at each Hewlett-Packard and Canon seen that ink would boil and splatter when uncovered to a scorching ingredient like a soldering iron, they usually determined to show that splattering right into a helpful inkjet printing mechanism. They knew {that a} resistor may very well be used as a heating ingredient and may very well be miniaturized with the identical know-how as that used for built-in circuits. Within the printers they constructed, every ink nozzle comprises a resistor as an alternative of a piezoelectric actuator. {An electrical} pulse heats the resistor, which flash-boils a skinny layer of the ink, forming a quickly increasing vapor bubble that pushes a droplet of ink out via the orifice.
This work led to 2 competing variations of thermal inkjet know-how coming to market at practically the identical time 40 years in the past. (The identical yr, 1984, Epson launched a stand-alone
piezoelectric inkjet printer.)
Hewlett-Packard’s
HP ThinkJet was its first desktop inkjet printer primarily based on its thermal know-how, and it was designed to hook up with a private laptop for on a regular basis printing. It had a right away benefit over the just lately developed laser printers: It was less expensive. A desktop laser printer from HP value US $3,500 (about $10,500 at this time); HP’s 2225A ThinkJet value solely $495 ($1,500 at this time). Inkjet printers additionally used far much less energy than laser printers did and had been quieter. Admittedly, inkjets didn’t have nice decision—96 dpi in contrast with 300 for laser printers in these early days—they usually had been gradual.
However the benefits outweighed the disadvantages (extra in order the know-how improved), and inkjet printers got here to dominate the desktop and residential printer markets. At present, greater than 20 corporations make inkjet printers, producing a market of
greater than $100 billion yearly and persevering with to develop at greater than 8 % per yr.
Printing DNA Microarrays With Inkjets
Whereas the enterprise of constructing inkjet printers matured and grew, some corporations started exploring what different kinds of “ink” is perhaps delivered with an inkjet. One in all these was Agilent Applied sciences, a spin-off of Hewlett Packard with a concentrate on life-science and chemical-analysis applied sciences. Agilent developed a method to print strands of DNA from the 4 nucleic acid bases—cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A), and thymine (T). Particularly, the corporate tailored present DNA chemistries plus inkjet printing strategies to construct
microarrays of DNA on glass slides for genomics work, resembling measuring which genes are being expressed in an organism beneath varied situations. Educational researchers have shared open-source strategies for changing present inkjet printers to construct their very own microarrays, albeit with specs which are far more modest than the industrial programs.
A DNA microarray consists of a substrate, normally glass, with an array of small areas known as spots the place DNA strands are connected. Agilent produces arrays with as many as 1,000,000 spots on a single 2.5-by-7.6-cm slide. An open-source system places as much as 10,000 in a considerably smaller space. Every DNA strand is manufactured from sequences of the bases C, G, A, and T. In double-stranded DNA, the strands have complementary sequences, which be a part of up like rungs of a ladder, C becoming a member of with G, and A with T.
A DNA microarray makes use of single-stranded DNA, and every spot has tens of millions of strands with a typical sequence. When a pattern with copies of the complementary strand washes over the spot, these strands bind along with the strands anchored within the spot. The pattern strands are tagged with fluorescent molecules, and the person learns which DNA sequences had been current within the pattern by inspecting which spots mild up.
In Agilent’s methodology for fabricating a microarray, the printer makes a number of passes over the substrate, every go including one base to every strand within the spots, with intermediate steps to organize for the subsequent go.
Including a base is definitely a three-step course of. Every of the rising strands within the microarray spots has a molecular “cap” on the finish that stops the indiscriminate addition of extra bases. So step one is to take away or deactivate these caps by washing an answer over the nascent microarray. The second step is analogous to printing a web page: At every spot on the microarray, the inkjet provides a dot of liquid containing the subsequent monomer molecule (modified variations of C, G, A, or T) to be added to the top of the strand. These monomers every embody a brand new cap in order that just one molecule will get added to every strand. Though the newly added monomers at the moment are connected to the strands, the connection is just not absolutely secure, and so the third step applies an oxidizer answer that modifies the bonds, absolutely integrating the brand new monomers into the DNA construction. Rinse and repeat.
The flexibility of the open-source inkjet building permits researchers to quickly construct prototype arrays with no matter sequences they wish to check out. A brand new array may be designed, synthesized, and used to investigate DNA in a single day.
One group reported a cycle time of 10 to twenty minutes to connect every base with their system, or about 13 hours to provide a batch of arrays, every with about 10,000 spots containing 40-base strands. For comparability’s sake, Agilent’s industrial microarrays usually have strands as much as 60 bases lengthy.
Agilent additionally makes use of its inkjet system to synthesize one other genomic workhorse often known as an
oligonucleotide library. The method is identical as for making a microarray, however on the finish all of the strands are cleaved from the substrate, dried, and packaged collectively in a single tube for the shopper. Agilent’s inkjet-printed libraries have strands as much as about 230 bases lengthy.
3D Printing Utilizing Two Inkjet Inks
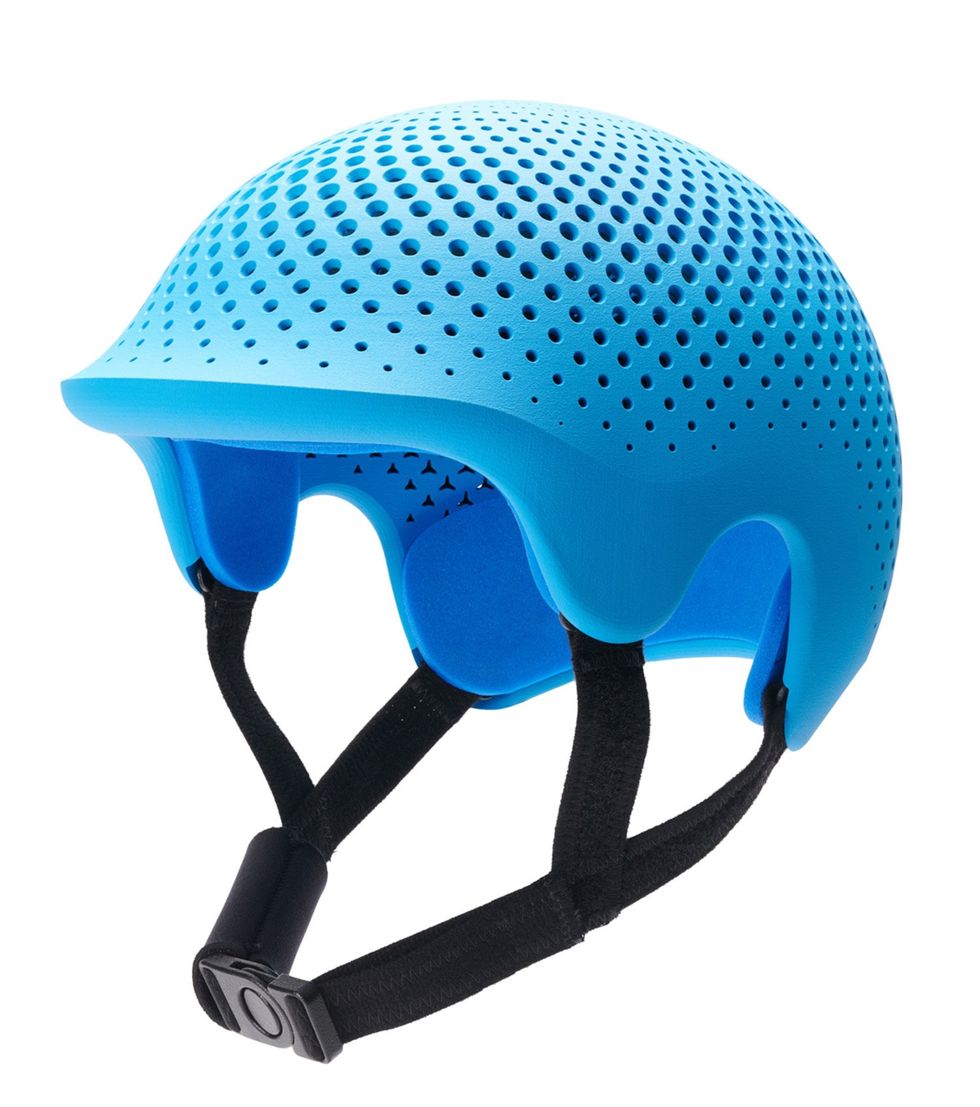
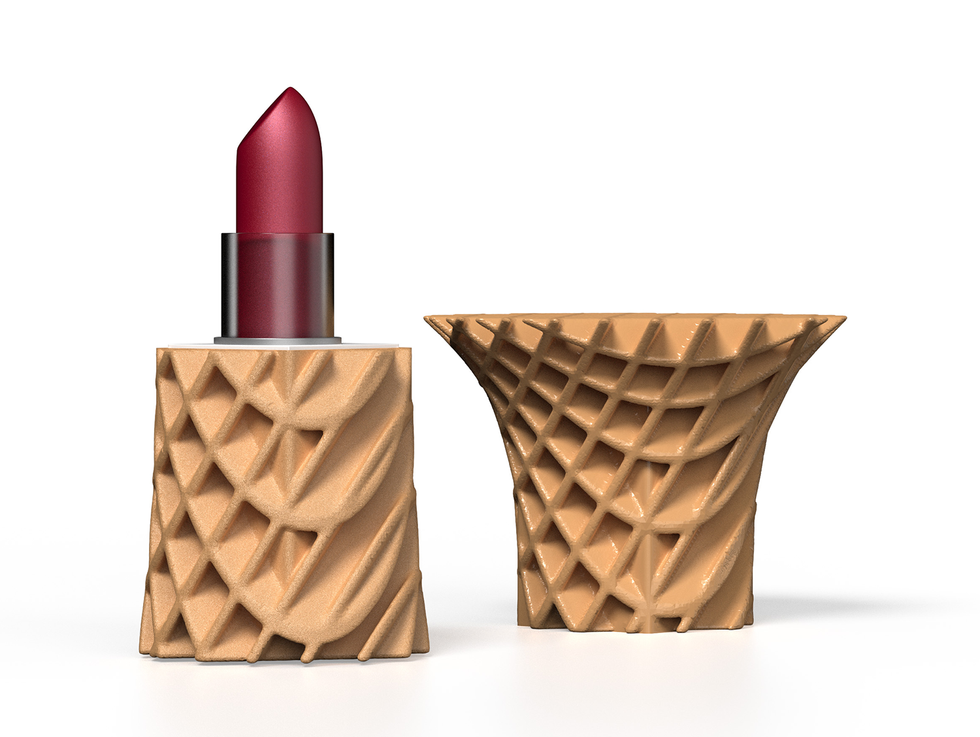
 Invent Medical—a Czech Republic startup partnered with HP—{custom} printed this helmet for correcting head-shape deformities [top]. An HP Jet Fusion 5200 printed this lipstick holder [bottom].High: Invent Medical/HP; backside: YOO Make-up/HP
Invent Medical—a Czech Republic startup partnered with HP—{custom} printed this helmet for correcting head-shape deformities [top]. An HP Jet Fusion 5200 printed this lipstick holder [bottom].High: Invent Medical/HP; backside: YOO Make-up/HP
Along with printing two-dimensional pages and constructing one-dimensional molecular strands, inkjet know-how has for a few years been used to provide three-dimensional objects. One strategy is a variant of powder-bed 3D printing, during which objects are constructed up by fusing or binding layers of powder within the desired sample. The inkjet printhead applies droplets of a liquid binding agent to every layer of powder within the areas that may type the completed 3D gadgets.
The HP Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) line of 3D printers extends this strategy by depositing two varieties of ink: One is a binding promoter and the opposite a detailing agent, which is utilized on the edges of the sample to forestall the promoter from bleeding into the encompassing powder. A printhead carrying a wide selection of inkjet nozzles dispenses these inks, and the array is rapidly adopted by a lighting bar to warmth the powder, fusing it within the areas the place the binding promoter is current. A contemporary layer of powder is then unfold over the whole printing space in readiness for the subsequent cycle of the method. On the finish, compressed air and a vacuum hose take away the unfused powder to disclose the finished 3D objects. The HP MJF printers carry out this in a quantity of as much as 38 by 28 by 38 cm.
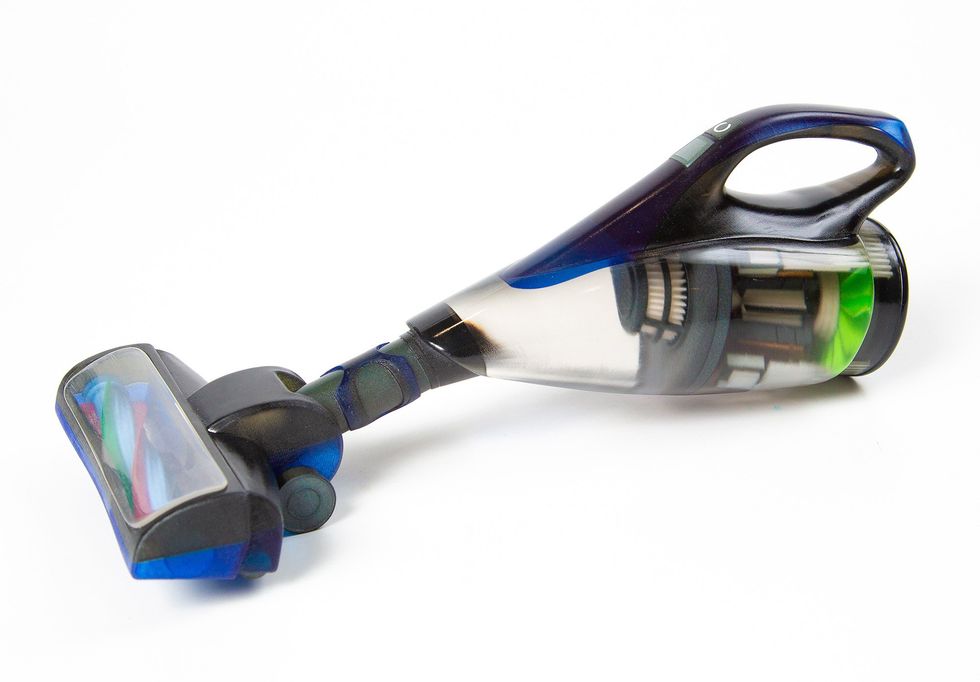 This mannequin of a handheld vacuum cleaner with coloured, translucent, and clear elements was printed in a single piece on a Mimaki inkjet 3D printer.Mimaki Engineering Co.
This mannequin of a handheld vacuum cleaner with coloured, translucent, and clear elements was printed in a single piece on a Mimaki inkjet 3D printer.Mimaki Engineering Co.
A fairly completely different strategy has been taken by
Mimaki Engineering Co. of Japan, which has launched 3D printers with piezoelectric inkjet heads that dispense droplets of resin. The resins are photopolymers which are cured by ultraviolet light-emitting diodes after every layer is printed. As an alternative of utilizing a powder mattress that fills the whole construct space, the printer deposits the resins on prime of the rising construction. To cope with steep overhangs—resembling an outstretched arm of a figurine—one of many resins produces a water-soluble materials, which is used to construct helps the place wanted. After the construct is completed, these helps may be dissolved away.
Seven different resins present colours that may embody CMYK—the acquainted cyan, magenta, yellow, and black inks of shopper inkjet printers—in addition to white and clear, for a complete of 10 million colour combos, similar to the colour depth that the human eye can discriminate. The ensuing elements can mix stable colour, coloured transparency and translucency, and colorless transparency.
The printer offers a quantity for constructing that measures 51 by 51 by 30 cm. In contrast to with a powder-bed machine, small take a look at elements may be made with out filling the whole quantity. Basically, nonetheless, the Mimaki strategy is slower than that of the HP MJF as a result of it makes use of smaller printheads as an alternative of a large one that may cross the whole space in a single sweep.
Inkjet’s Future
Inkjet printing’s energy is the flexibility to sample varied inks over massive areas briefly, speedy manufacturing runs at an affordable value. It can’t usually compete with customary high-volume manufacturing approaches, as a result of these will normally be cheaper. Thus, a automobile fanatic, for example, could embrace 3D inkjet printing to make bespoke elements for repairs or different tinkering, however a high-volume car-parts producer is just not going to introduce such printers to its manufacturing facility strains. Equally, an organization could construct particular person collectible figurines from a buyer’s design, printed by 3D inkjet, however the identical method gained’t be economical for mass-producing fashions of the most recent superhero. With many potential functions, it isn’t clear if there’s a area of interest the place the inkjet strategy will win.
An instance is the usage of 3D inkjet printing for
personalised medication. The concept is to provide tablets of a drugs custom-made for a particular affected person. Such personalised tablets can embody easy fine-tuning of the dose for a person, in addition to changes to the drug’s launch charge—from very speedy to gradual and sustained—via modifications to the binding brokers and construction of the pill. Relatively than juggling a number of drugs on a sophisticated schedule every day, a affected person might take a single each day polypill—a 3D-printed pill containing a number of drugs, every with a distinct charge of launch.
Researchers are exploring tips on how to adapt present 3D printing strategies, together with inkjet, to make these personalised drugs. Inkjet programs are significantly suited to printing medicine within the type of skinny movies, resembling transdermal patches to be utilized to the pores and skin and buccal movies to be held within the cheek, the place medicine can go on to the bloodstream with out first going via the digestive system.
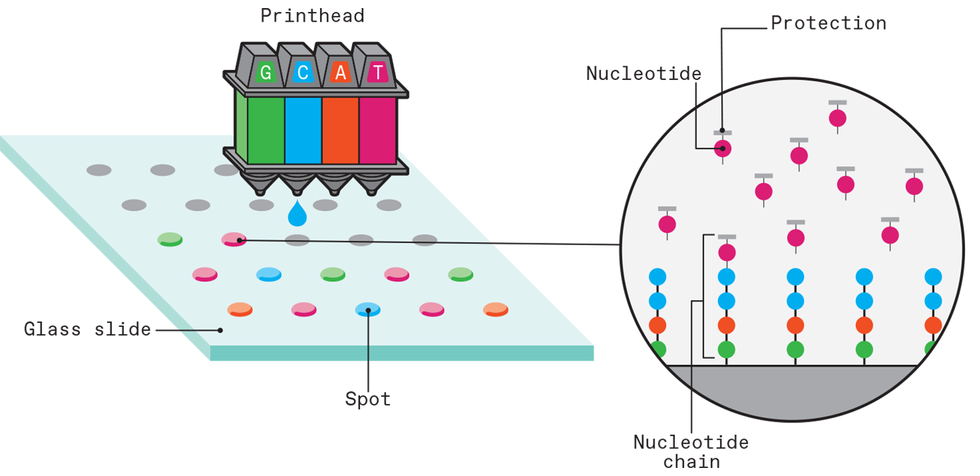 A DNA microarray may be fabricated utilizing an inkjet system to construct custom-designed strands of DNA at every spot of the array. The printhead delivers a droplet of “ink” [left] containing modified monomers of 1 nucleotide [G, C, A, or T] to every spot. On the primary print cycle, these monomers connect to the chemically handled glass floor. On subsequent print runs [right], a single monomer joins on the top of every rising DNA strand. Every monomer features a protecting cap to forestall different monomers from becoming a member of. Extra processes [not depicted here] wash away the nucleotide ink, apply a catalyst to finish the monomer bonding, and strip away the protecting caps in preparation for the subsequent printing step.Chris Philpot
A DNA microarray may be fabricated utilizing an inkjet system to construct custom-designed strands of DNA at every spot of the array. The printhead delivers a droplet of “ink” [left] containing modified monomers of 1 nucleotide [G, C, A, or T] to every spot. On the primary print cycle, these monomers connect to the chemically handled glass floor. On subsequent print runs [right], a single monomer joins on the top of every rising DNA strand. Every monomer features a protecting cap to forestall different monomers from becoming a member of. Extra processes [not depicted here] wash away the nucleotide ink, apply a catalyst to finish the monomer bonding, and strip away the protecting caps in preparation for the subsequent printing step.Chris Philpot
These printed personalised medicines, nonetheless, could be costly in comparison with fastened doses rolling off customary high-volume manufacturing strains. Thus the method is prone to be reserved for comparatively uncommon situations.
One other potential software of 3D inkjet printing is within the fabrication of superior lithium-ion batteries. The charging and discharging of those batteries depends on lithium ions transferring from the battery’s electrodes to its electrolyte and again once more, within the course of releasing or absorbing electrons that produce the present stream. The energy-storage density of the usual electrode design may be elevated through the use of thicker electrodes, however this compromises the facility density—the speed of power launch—as a result of a smaller proportion of the electrode is in shut contact with the electrolyte.
A 3D inkjet might construct electrodes with an in depth microstructure that permits the electrolyte to penetrate all through the electrode quantity. This might increase the flexibility of the lively lithium ions and electrons to succeed in the whole electrode effectively even when the electrode is bigger, thereby rising the power storage and energy density in tandem. For this imaginative and prescient to develop into a actuality, nonetheless, researchers might want to be taught extra about tips on how to formulate the “inks” for printing these electrodes: What are the most effective particle sizes and solvents to make an ink with fluid properties appropriate to be used in an inkjet system and that may produce secure printed constructions with good electrochemical properties?
We expect it’s unlikely, nonetheless, that inkjet printing might compete with high-volume manufacturing on value. Inkjet printing of prototypes, however, could uncover an optimum battery design that may then be tailored for manufacturing by typical strategies.
Inkjet programs have been demonstrated for all kinds of functions past what we now have mentioned above:
Residing cells may be printed, for example, to type tissue constructions for in vitro experiments. MEMS resembling microscopic motors have been printed utilizing inks containing nanoparticles of gold and silver as conductors and resin-based inks to behave as insulators. Versatile sensors for well being care monitoring have been printed utilizing an electrically conducting polymer that responds to temperature differentials. After which there are all of the methods inkjets are used to create pictures on media aside from workplace printouts, resembling printing of textiles, inkjet robots to use {custom} automotive paint jobs, and the “Giclée” printing of high-quality artwork utilizing archival-quality inks and substrates.
Every of those functions is sort of a coloured dot on the huge canvas of human know-how and exercise. And whereas the dots from inkjets, powered by MEMS, could also be solely a single colour amongst many others on that metaphorical web page, the image could be very completely different with out them.
From Your Website Articles
Associated Articles Across the Internet
