
NASA is searching for methods to get rock samples again from Mars for lower than the $11 billion the company would want below its personal plan, so final month, officers put out a name to trade to suggest concepts.
Boeing is the primary firm to launch particulars about how it might try a Mars Pattern Return mission. Its research entails a single flight of the Area Launch System (SLS) rocket, the tremendous heavy-lift launcher designed to ship astronauts to the Moon on NASA’s Artemis missions.
Jim Inexperienced, NASA’s former chief scientist and longtime head of the company’s planetary science division, introduced Boeing’s idea Wednesday on the People to Mars summit, an annual occasion sponsored primarily by conventional house corporations. Boeing is the lead contractor for the SLS core stage and higher stage and has pitched the SLS, primarily a crew launch automobile, as a rocket for navy satellites and deep house probes.
Multi function
Inexperienced, now retired, stated the idea he and Boeing engineers suggest would cut back the dangers of Mars Pattern Return. With one mission, there are fewer factors of potential failure, he stated.
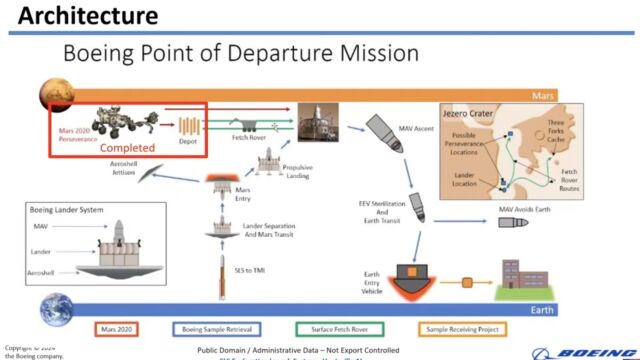
“To scale back mission complexity, this new idea is doing one launch,” Inexperienced stated.
This argument makes some sense, however the issue is SLS is the costliest rocket flying at the moment. Even when NASA and Boeing introduce cost-cutting measures, NASA’s inspector basic reported final yr it is unlikely the price of a single SLS launch would fall under $2 billion. The inspector basic advisable NASA take into account shopping for industrial rockets as an alternative choice to SLS for future Artemis missions.
NASA’s Perseverance rover, working on Mars since February 2021, is accumulating soil and rock core samples and sealing them in 43 cigar-size titanium tubes. The rover has dropped the primary 10 of those tubes in a depot on the Martian floor that might be retrieved by a future pattern return mission. The remaining tubes will probably stay stowed on Perseverance in hopes the rover will straight hand off the samples to the spacecraft that involves Mars to get them.
Boeing
In his remarks, Inexperienced touted the advantages of launching a Mars Pattern Return mission with a single rocket and a single spacecraft. NASA’s baseline idea entails two launches, one with a US-built lander and a small rocket to spice up the rocket samples again off the floor of Mars, and one other with a European spacecraft to rendezvous with the pattern service in orbit round Mars, then deliver the specimens again to Earth.
“This idea is one launch automobile,” he stated. “It is the SLS. What does it do? It is carrying an enormous payload. What’s the payload? It is a Mars entry and descent aeroshell. It has a propulsive descent module.”
The lander would carry all the pieces wanted to get the samples again to Earth. A fetch rover onboard the lander would deploy to drive out and choose up the pattern tubes collected by the Perseverance rover. Then, a robotic arm would switch the pattern tubes to a container on the high of a two-stage rocket referred to as the Mars Ascent Automobile (MAV) sitting on high of the lander. The MAV would have the oomph wanted to spice up the samples off the floor of Mars and into orbit, then hearth engines to focus on a course again to Earth.
Boeing has no direct expertise as a first-rate contractor for any Mars mission. SpaceX, with its large Starship rocket designed for eventual Mars missions, and Lockheed Martin, which has constructed a number of Mars landers for NASA, are the businesses with the expertise and experience that appear to be most helpful for Mars Pattern Return.
NASA can be accumulating concepts for Mars Pattern Return from its house facilities throughout america. The company additionally tasked the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which was in command of growing the unique dead-on-arrival idea, to give you a greater concept. Later this yr, NASA officers will reference these new proposals as they resolve easy methods to proceed with Mars Pattern Return, with the objective of getting samples again from Mars within the 2030s.

