The accelerating buildout of photo voltaic farms on Earth is already hitting pace bumps, together with public pushback towards the big tracts of land required and a ballooning backlog of requests for brand spanking new transmission traces and grid connections. Vitality specialists have been warning that electrical energy is prone to get dearer and fewer dependable except renewable energy that waxes and wanes underneath inconstant daylight and wind is backed up by turbines that may run every time wanted. To area fanatics, that raises an apparent query: Why not stick solar energy crops the place the solar all the time shines?
Area-based solar energy is an concept so lovely, so tantalizing that some argue it’s a want value fulfilling. A constellation of gigantic satellites in geosynchronous orbit (GEO) almost 36,000 kilometers above the equator may accumulate daylight unfiltered by environment and uninterrupted by evening (apart from as much as 70 minutes a day across the spring and fall equinoxes). Every megasat may then convert gigawatts of energy right into a microwave beam aimed exactly at an enormous discipline of receiving antennas on Earth. These rectennas would then convert the sign to usable DC electrical energy.
The hundreds of rocket launches wanted to loft and preserve these area energy stations would dump a lot of soot, carbon dioxide, and different pollution into the stratosphere, with unsure local weather impacts. However that may be mitigated, in principle, if area photo voltaic displaced fossil fuels and helped the world transition to wash electrical energy.
The glamorous imaginative and prescient has impressed quite a few futuristic proposals. Japan’s area company has offered a highway map to deployment. Area authorities in China goal to place a small check satellite tv for pc in low Earth orbit (LEO) later this decade. Concepts to place megawatt-scale methods in GEO someday within the 2030s have been floated however not but funded.
The U.S. Naval Analysis Laboratory has already beamed greater than a kilowatt of energy
between two floor antennas a few kilometer aside. It additionally launched in 2023 a satellite tv for pc that used a laser to transmit about 1.5 watts, though the beam traveled lower than 2 meters and the system had simply 11 % effectivity. A workforce at Caltech earlier this yr wrapped up a mission that used a small satellite tv for pc in LEO to check thin-film photo voltaic cells, versatile microwave-power circuitry, and a small collapsible deployment mechanism. The vitality despatched Earthward by the craft was too meager to energy a lightbulb, however it was progress nonetheless.
The European Area Company (ESA) debuted in 2022 its space-based solar-power program, referred to as Solaris, with an inspiring (however completely fantastical)
video animation. This system’s director, Sanjay Vijendran, informed IEEE Spectrum that the aim of the hassle is to not develop an influence station for area. As a substitute, this system goals to spend three years and €60 million (US $65 million) to determine whether or not photo voltaic cells, DC-to-RF converters, meeting robots, beam-steering antennas, and different must-have applied sciences will enhance drastically sufficient over the subsequent 10 to twenty years to make orbital solar energy possible and aggressive. Low-cost, low-mass, and space-hardy variations of those applied sciences can be required, however engineers making an attempt to attract up detailed plans for such satellites right now discover no components that meet the powerful necessities.
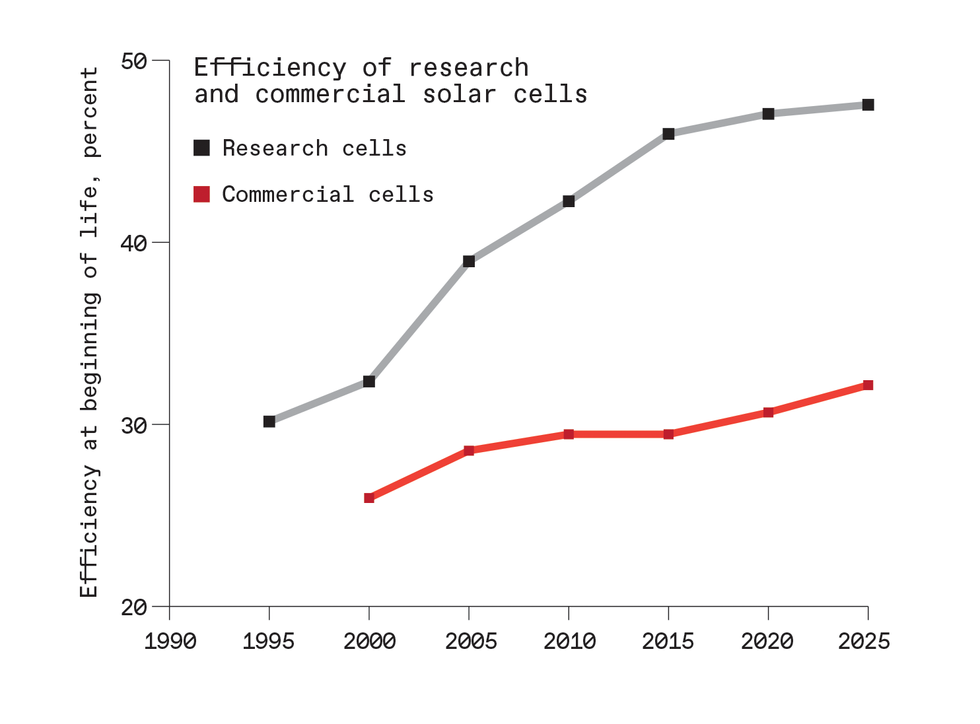 Not so quick: The true-world effectivity of business, space-qualified photo voltaic cells has progressed way more slowly than information set in extremely managed analysis experiments, which frequently use unique supplies or complicated designs that can’t presently be mass-produced. Factors plotted right here present the best effectivity reported in five-year intervals.HENRI BARDE; DATA FROM NATIONAL RENEWABLE ENERGY LABORATORY (RESEARCH CELLS) AND FROM MANUFACTURER DATA SHEETS AND PRESENTATIONS (COMMERCIAL CELLS)
Not so quick: The true-world effectivity of business, space-qualified photo voltaic cells has progressed way more slowly than information set in extremely managed analysis experiments, which frequently use unique supplies or complicated designs that can’t presently be mass-produced. Factors plotted right here present the best effectivity reported in five-year intervals.HENRI BARDE; DATA FROM NATIONAL RENEWABLE ENERGY LABORATORY (RESEARCH CELLS) AND FROM MANUFACTURER DATA SHEETS AND PRESENTATIONS (COMMERCIAL CELLS)
With the flurry of renewed consideration, you would possibly marvel: Has extraterrestrial solar energy lastly discovered its second? Because the just lately retired head of area energy methods at ESA—with greater than 30 years of expertise engaged on energy technology, vitality storage, and electrical methods design for dozens of missions, together with analysis of a power-beaming experiment proposed for the Worldwide Area Station—I believe the reply is sort of definitely no.
Regardless of mounting buzz across the idea, I and plenty of of my former colleagues at ESA are deeply skeptical that these massive and complicated energy methods could possibly be deployed shortly sufficient and extensively sufficient to make a significant contribution to the worldwide vitality transition. Among the many many challenges on the lengthy and formidable listing of technical and societal obstacles: antennas so massive that we can’t even simulate their conduct.
Right here I supply a highway map of the potential chasms and useless ends that would doom a untimely area photo voltaic mission to failure. Such a misadventure would undermine the credibility of the accountable area company and waste capital that could possibly be higher spent bettering much less dangerous methods to shore up renewable vitality, akin to batteries, hydrogen, and grid enhancements. Champions of area solar energy may take a look at this highway map as a want listing that have to be fulfilled earlier than orbital solar energy can change into actually interesting to electrical utilities.
Area Photo voltaic Energy at Peak Hype—Once more
For many years, enthusiasm for the opportunity of drawing limitless, largely clear energy from the one fusion reactor we all know works reliably—the solar—has run cold and warm. A
1974 examine that NASA commissioned from the consultancy Arthur D. Little bullishly advisable a 20-year federal R&D program, anticipated to result in a business station launching within the mid-Nineteen Nineties. After 5 years of labor, the company delivered a reference structure for as much as 60 orbiting energy stations, every delivering 5 to 10 gigawatts of baseload energy to main cities. However officers gave up on the thought once they realized that it might price over $1 trillion (adjusted for inflation) and require tons of of astronauts working in area for many years, all earlier than the primary kilowatt could possibly be offered.
NASA didn’t severely rethink area photo voltaic till 1995, when it ordered
a “recent look” on the risk. That two-year examine generated sufficient curiosity that the U.S. Congress funded a small R&D program, which printed plans to place up a megawatt-scale orbiter within the early 2010s and a full-size energy plant within the early 2020s. Funding was minimize off a couple of years later, with no satellites developed.
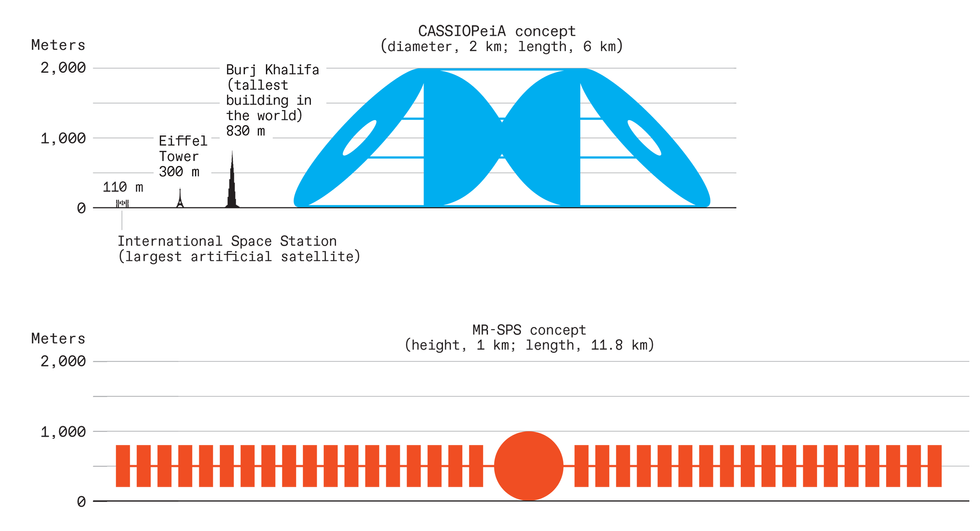 Due to the physics of energy transmission from geosynchronous orbit, area energy satellites have to be monumental—tons of of occasions bigger than the Worldwide Area Station and even dwarfing the tallest skyscrapers—to generate electrical energy at a aggressive value. The challenges for his or her engineering and meeting are equally gargantuan. Chris Philpot
Due to the physics of energy transmission from geosynchronous orbit, area energy satellites have to be monumental—tons of of occasions bigger than the Worldwide Area Station and even dwarfing the tallest skyscrapers—to generate electrical energy at a aggressive value. The challenges for his or her engineering and meeting are equally gargantuan. Chris Philpot
Then, a decade in the past, private-sector startups generated one other flurry of media consideration. One, Solaren, even signed a power-purchase settlement to ship 200 megawatts to utility clients in California by 2016 and made
daring predictions that area photo voltaic crops would enter mass manufacturing within the 2020s. However the contract and guarantees went unfulfilled.
The repeated hype cycles have ended the identical method every time, with buyers and governments balking on the large investments that have to be risked to construct a system that can not be assured to work. Certainly, in what may presage the top of the present hype cycle, Solaris managers have had hassle drumming up curiosity amongst ESA’s 22 member states. Up to now solely the UK has participated, and simply 5 % of the funds accessible have been dedicated to precise analysis work.
Even space-solar advocates have acknowledged that success clearly hinges on one thing that can not be engineered: sustained political will to speculate, and hold investing, in a multidecade R&D program that finally may yield machines that may’t put electrical energy on the grid. In that respect, beamed energy from area is like nuclear fusion, besides no less than 25 years behind.
Within the Nineteen Nineties, the fusion neighborhood succeeded in tapping into nationwide protection budgets and cobbled collectively the 35-nation, $25 billion megaproject ITER, which launched in 2006. The trouble set information for delays and price overruns, and but a prototype remains to be years from completion. Nonetheless, dozens of startups are actually testing new fusion-reactor ideas. Large investments in area photo voltaic would doubtless proceed in the identical method. After all, if fusion succeeds, it might eclipse the rationale for solar-energy satellites.
Area Business Specialists Run the Numbers
The U.S. and European area companies have just lately launched detailed technical analyses of a number of space-based solar-power proposals. [See diagrams.] These stories make for sobering studying.
Electrical energy made this fashion,
NASA reckoned in its 2024 report, would initially price 12 to 80 occasions as a lot as energy generated on the bottom, and the primary energy station would require no less than $275 billion in capital funding. Ten of the 13 essential subsystems required to construct such a satellite tv for pc—together with gigawatt-scale microwave beam transmission and robotic building of kilometers-long, high-stiffness buildings in area—rank as “excessive” or “very excessive” technical issue, in line with a 2022 report back to ESA by Frazer-Nash, a U.Ok. consultancy. Plus, there isn’t any identified solution to safely get rid of such monumental buildings, which might share an more and more crowded GEO with essential protection, navigation, and communications satellites, notes a 2023 ESA examine by the French-Italian satellite tv for pc maker Thales Alenia Area.
A substitute for microwave transmission can be to beam the vitality all the way down to Earth as mirrored daylight. Engineers at Arthur D. Little described the idea in
a 2023 ESA examine through which they proposed encircling the Earth with about 4,000 aimable mirrors in LEO. As every satellite tv for pc zips overhead, it might shine an 8-km-wide highlight onto taking part photo voltaic farms, permitting the farms to function a couple of additional hours every day (if skies are clear). Along with the issues of clouds and lightweight air pollution, the report famous the thorny challenge of orbital particles, estimating that every reflector can be penetrated about 75 billion occasions throughout its 10-year working life.
My very own evaluation, offered on the 2023 European Area Energy Convention and
printed by IEEE, identified doubtful assumptions and inconsistencies in 4 space-solar designs which have acquired severe consideration from authorities companies. Certainly, the ideas detailed thus far all appear to face on shaky technical floor.
Large Transmitters and Receiving Stations
The excessive prices and arduous engineering issues that forestall us from constructing orbital solar-power methods right now come up primarily from the enormity of those satellites and their distance from Earth, each of that are unavoidable penalties of the physics of this type of vitality transmission. Solely in GEO can a satellite tv for pc keep (nearly) repeatedly linked to a single receiving station on the bottom. The methods should beam down their vitality at a frequency that passes comparatively unimpeded by means of all types of climate and doesn’t intervene with crucial radio methods on Earth. Most designs name for two.45 or 5.8 gigahertz, inside the vary used for Wi-Fi. Diffraction will trigger the beam to unfold because it travels, by an quantity that will depend on the frequency.
Thales Alenia Area estimated {that a} transmitter in GEO have to be no less than 750 meters in diameter to coach the intense middle of a 5.8-GHz microwave beam onto a floor station of affordable space over that great distance—65 occasions the altitude of LEO satellites like Starlink. Even utilizing a 750-meter transmitter, a receiver station in France or the northern United States would fill an elliptical discipline masking greater than 34 sq. kilometers. That’s greater than two-thirds the scale of Bordeaux, France, the place I stay.
“Success hinges on one thing that can not be engineered: sustained political will to maintain investing in a multidecade R&D program that finally may yield machines that may’t put electrical energy on the grid.”
Large parts include large lots, which result in exorbitant launch prices. Thales Alenia Area estimated that the transmitter alone would weigh no less than 250 tonnes and price properly over a billion {dollars} to construct, launch, and ferry to GEO. That estimate, primarily based on concepts from the Caltech group which have but to be examined in area, appears wildly optimistic; earlier detailed transmitter designs are about 30 occasions heavier.
As a result of the transmitter must be massive and costly, any orbiting photo voltaic mission will maximize the ability it sends by means of the beam, inside acceptable security limits. That’s why the methods evaluated by NASA, ESA, China, and Japan are all scaled to ship 1–2 GW, the utmost output that utilities and grid operators now say they’re keen to deal with. It will take two or three of those large satellites to exchange one massive retiring coal or nuclear energy station.
Vitality is misplaced at every step within the conversion from daylight to DC electrical energy, then to microwaves, then again to DC electrical energy and eventually to a grid-compatible AC present. Will probably be arduous to enhance a lot on the 11 % end-to-end effectivity seen in latest discipline trials. So the photo voltaic arrays and electrical gear have to be sufficiently big to gather, convert, and distribute round 9 GW of energy in area simply to ship 1 GW to the grid. No digital switches, relays, and transformers have been designed or demonstrated for spacecraft that may deal with voltages and currents wherever close to the required magnitude.
Some area photo voltaic designs, akin to
SPS-ALPHA and CASSIOPeiA, would droop large reflectors on kilometers-long booms to pay attention daylight onto high-efficiency photo voltaic cells on the again facet of the transmitter or intermingled with antennas. Different ideas, akin to China’s MR-SPS and the design proposed by Thales Alenia Area, would ship the currents by means of heavy, motorized rotating joints that enable the big photo voltaic arrays to face the solar whereas the transmitter pivots to remain mounted on the receiving station on Earth.
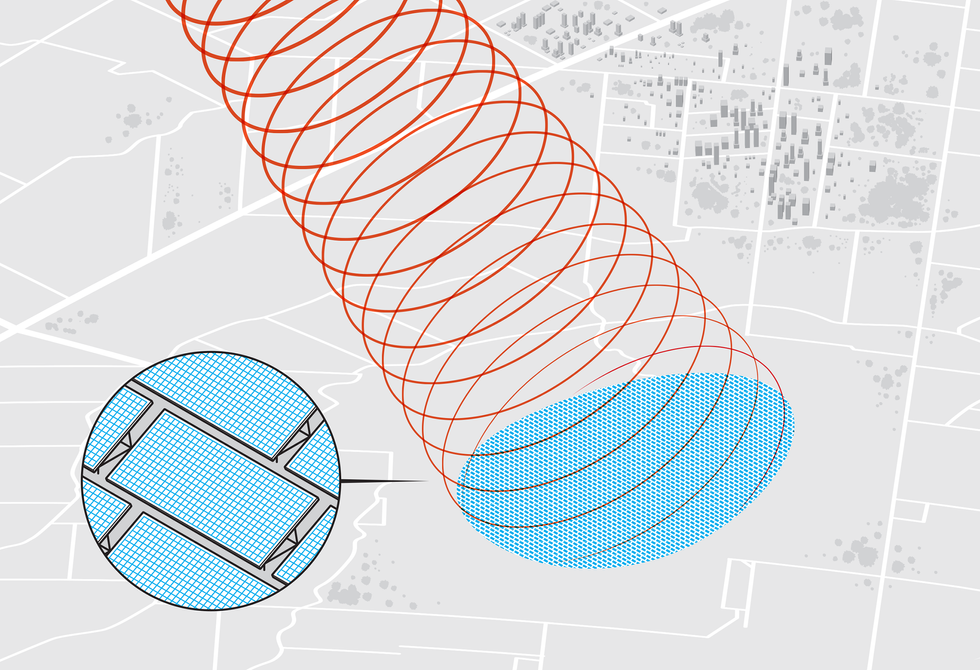 All area solar-power ideas that ship vitality to Earth by way of a microwave beam would want a big receiving station on the bottom. An elliptical rectenna discipline 6 to 10 kilometers large can be coated with antennas and electronics that rectify the microwaves into DC energy. Further inverters would then convert the electrical energy to grid-compatible AC present.Chris Philpot
All area solar-power ideas that ship vitality to Earth by way of a microwave beam would want a big receiving station on the bottom. An elliptical rectenna discipline 6 to 10 kilometers large can be coated with antennas and electronics that rectify the microwaves into DC energy. Further inverters would then convert the electrical energy to grid-compatible AC present.Chris Philpot
The online end result, no matter method, is an orbiting energy station that spans a number of kilometers, totals many hundreds of tonnes, sends gigawatts of steady energy by means of onboard electronics, and includes as much as one million modules that have to be assembled in area—by robots. That may be a gigantic leap from the most important satellite tv for pc and photo voltaic array ever constructed in orbit: the 420-tonne, 109-meter Worldwide Area Station (ISS), whose 164 photo voltaic panels produce lower than 100 kilowatts to energy its 43 modules.
The ISS has been constructed and maintained by astronauts, drawing on 30 years of prior expertise with the Salyut, Skylab, and Mir area stations. However there isn’t any comparable incremental path to a robot-assembled energy satellite tv for pc in GEO. Efficiently beaming down a couple of megawatts from LEO can be a formidable achievement, however it wouldn’t show {that a} full-scale system is possible, nor would the intermittent energy be significantly attention-grabbing to business utilities.
T Minus…Many years?
NASA’s 2024 report used sensitivity evaluation to search for advances, nevertheless implausible, that will allow orbital solar energy to be commercially aggressive with nuclear fission and different low-emissions energy. To begin, the worth of sending a tonne of cargo to LEO on a big reusable rocket, which has fallen 36 % over the previous 10 years, must drop by one other two-thirds, to $500,000. This assumes that each one the items of the station could possibly be dropped off in low orbit after which raised to GEO over a interval of months by area tugs propelled by electrical ion thrusters fairly than typical rockets. The method would gradual the tempo of building and add to the general mass and price. New tugs must be developed that would tow as much as 100 occasions as a lot cargo as the most important electrical tugs do right now. And by my calculations, the world’s annual manufacturing of xenon—the go-to propellant for ion engines—is inadequate to hold even a single solar-power satellite tv for pc to GEO.
Thales Alenia Area checked out a barely extra lifelike choice: utilizing a fleet of typical rockets as massive as SpaceX’s new Starship—the most important rocket ever constructed—to ferry hundreds from LEO to GEO, after which again to LEO for refueling from an orbiting gas depot. Even when launch costs plummeted to $200,000 a tonne, they calculated, electrical energy from their system can be six occasions as costly as NASA’s projected price for a terrestrial photo voltaic farm outfitted with battery storage—one apparent various.
What else must go spectacularly proper? In NASA’s cost-competitive situation, the worth of recent, specialised spaceships that would preserve the satellite tv for pc for 30 years—after which disassemble and get rid of it—must come down by 90 %. The effectivity of commercially produced, space-qualified photo voltaic cells must soar from 32 % right now to 40 %, whereas falling in price. But over the previous 30 years, massive features within the effectivity of analysis cells haven’t translated properly to the business cells accessible at low price [see chart, “Not So Fast”].
Is it attainable for all these items to go proper concurrently? Maybe. However wait—there’s extra that may go improper.
The Toll of Working a Photo voltaic Plant in Area
Let’s begin with temperature. Gigawatts of energy coursing by means of the system will make warmth removing important as a result of photo voltaic cells lose effectivity and microcircuits fry once they get too scorching. A few dozen occasions a yr, the satellite tv for pc will move out of the blue into the utter darkness of Earth’s shadow, inflicting temperatures to swing by round 300 °C, properly past the standard working vary of electronics. Thermal growth and contraction might trigger massive buildings on the station to warp or vibrate.
Then there’s the bodily toll of working in area. Vibrations and torques exerted by altitude-control thrusters, plus the strain of photo voltaic radiation on the huge sail-like arrays, will frequently bend and twist the station this fashion and that. The sprawling arrays will endure unavoidable strikes from man-made particles and micrometeorites, maybe even a malfunctioning building robotic. Because the variety of area energy stations will increase, we may see a fast rise in the specter of
Kessler syndrome, a runaway cascade of collisions that’s each area operator’s nightmare.
In all probability the hardest technical impediment blocking area solar energy is a primary one: shaping and aiming the beam. The transmitter is just not a dish, like a radio telescope in reverse. It’s a phased array, a set of tens of millions of little antennas that should work in near-perfect synchrony, every contributing its piece to a collective waveform aimed on the floor station.
Like folks in a stadium crowd elevating their arms on cue to do “the wave,” coordination of a phased array is important. It’s going to work correctly provided that each aspect on the emitter syncs the part of its transmission to align exactly with the transmission of its neighbors and with an incoming beacon sign despatched from the bottom station. Section errors measured in picoseconds could cause the microwave beam to blur or drift off its goal. How can the system synchronize components separated by as a lot as a kilometer with such unbelievable accuracy? When you’ve got the reply, please patent and publish it, as a result of this drawback presently has engineers stumped.
There is no such thing as a denying the fantastic thing about the thought of turning to deep area for inexhaustible electrical energy. However nature will get a vote. As Lao Tzu noticed way back within the
Tao Te Ching, “The reality is just not all the time lovely, nor lovely phrases the reality.”
From Your Website Articles
Associated Articles Across the Internet

