Plenty of insights and opinions have already been shared about final week’s leak of Google’s Content material API Warehouse documentation, together with the incredible write-ups from:
However what can hyperlink builders and digital PRs study from the paperwork?
Since information of the leak broke, Liv Day, Digitaloft’s web optimization Lead, and I’ve spent plenty of time investigating what the documentation tells us about hyperlinks.
We went into our evaluation of the paperwork attempting to achieve insights round a number of key questions:
- Do hyperlinks nonetheless matter?
- Are some hyperlinks extra more likely to contribute to web optimization success than others?
- How does Google outline hyperlink spam?
To be clear, the leaked documentation doesn’t comprise confirmed rating components. It incorporates data on greater than 2,500 modules and over 14,000 attributes.
We don’t know the way these are weighted, that are utilized in manufacturing and which may exist for experimental functions.
However that doesn’t imply the insights we achieve from these aren’t helpful. As long as we take into account any findings to be issues that Google may be rewarding or demoting quite than issues they are, we will use them to type the premise of our personal assessments and are available to our personal conclusions about what’s or isn’t a rating issue.
Under are the issues we discovered within the paperwork that hyperlink builders and digital PRs ought to pay shut consideration to. They’re based mostly alone interpretation of the documentation, alongside my 15 years of expertise as an web optimization.
1. Google might be ignoring hyperlinks that don’t come from a related supply
Relevancy has been the most well liked matter in digital PR for a very long time, and one thing that’s by no means been simple to measure. In spite of everything, what does relevancy actually imply?
Does Google ignore hyperlinks that don’t come from inside related content material?
The leaked paperwork undoubtedly counsel that that is the case.
We see a transparent anchorMismatchDemotion referenced within the CompressedQualitySignals module:


Whereas we’ve got little additional context, what we will infer from that is that there’s the flexibility to demote (ignore) hyperlinks when there’s a mismatch. We are able to assume this to imply a mismatch between the supply and goal pages, or the supply web page and goal area.
What may the mismatch be, aside from relevancy?
Particularly after we take into account that, in the identical module, we additionally see an attribute of topicEmbeddingsVersionedData.


Matter embeddings are generally utilized in pure language processing (NLP) as a method of understanding the semantic that means of matters inside a doc. This, within the context of the documentation, means webpages.
We additionally see a webrefEntities attribute referenced within the PerDocData module.


What’s this? It’s the entities related to a doc.
We are able to’t make certain precisely how Google is measuring relevancy, however we may be fairly sure that the anchorMismatchDemotion includes ignoring hyperlinks that don’t come from related sources.
The takeaway?
Relevancy ought to be the most important focus when incomes hyperlinks, prioritized over just about some other metric or measure.
2. Regionally related hyperlinks (from the identical nation) are in all probability extra invaluable than ones from different nations
The AnchorsAnchorSource module, which supplies us an perception into what Google shops concerning the supply web page of hyperlinks, means that native relevance may contribute to the hyperlink’s worth.
Inside this doc is an attribute referred to as localCountryCodes, which shops the nations to which the web page is native and/or probably the most related.


It’s lengthy been debated in digital PR whether or not hyperlinks coming from websites in different nations and languages are invaluable. This offers us some indication as to the reply.
At the start, you need to prioritize incomes hyperlinks from websites which can be regionally related. And if we take into consideration why Google would possibly weigh these hyperlinks stronger, it makes complete sense.
Regionally related hyperlinks (don’t confuse this with native publications that usually safe hyperlinks and protection from digital PR; right here we’re speaking about country-level) usually tend to improve model consciousness, end in gross sales and be extra correct endorsements.
Nonetheless, I don’t imagine hyperlinks from different locales are dangerous. Greater than these the place the country-level relevancy matches are weighted extra strongly.
3. Google has a sitewide authority rating, regardless of claiming they don’t calculate an authority measure like DA or DR
Perhaps the most important shock to most SEOs studying the documentation is that Google has a “website authority” rating, regardless of stating time and time once more that they haven’t any measure that’s like Moz’s Area Authority (DA) or Ahrefs’ Area Ranking (DR).
In 2020, Google’s John Mueller acknowledged:
- “Simply to be clear, Google doesn’t use Area Authority *in any respect* relating to Search crawling, indexing, or rating.”
However later that yr, did trace at a sitewide measure, saying about Area Authority:
- “I don’t know if I’d name it authority like that, however we do have some metrics which can be extra on a website stage, some metrics which can be extra on a web page stage, and a few of these site-wide stage metrics would possibly type of map into comparable issues.”
Clear as day, within the leaked paperwork, we see a SiteAuthority rating.


To caveat this, although, we don’t know that that is even remotely in keeping with DA or DR. It’s additionally doubtless why Google has usually answered questions in the best way they’ve about this matter.
Moz’s DA and Ahrefs’ DR are link-based scores based mostly on the standard and amount of hyperlinks.
I’m uncertain that Google’s siteAuthority is solely link-based although, provided that feels nearer to PageRank. I’d be extra inclined to counsel that that is some type of calculated rating based mostly on page-level high quality scores, together with click on information and different NavBoost indicators.
The chances are, regardless of having the same naming conference, this doesn’t align with DA and DR, particularly provided that we see this referenced within the CompressedQualitySignals module, not a link-specific one.
4. Hyperlinks from inside newer pages are in all probability extra invaluable than these on older ones
One fascinating discovering is that hyperlinks from newer pages look to be weighted extra strongly than these coming from older content material, in some instances.
We see reference to sourceType within the context of anchors (hyperlinks), the place the standard of a hyperlink’s supply web page is recorded in correlation to the web page’s index tier.


What stands out right here, although, is the reference to newly revealed content material (freshdocs) being a particular case and regarded to be the identical as “prime quality” hyperlinks.
We are able to clearly see that the supply kind of a hyperlink can be utilized as an significance indicator, which means that this pertains to how hyperlinks are weighted.
What we should take into account, although, is {that a} hyperlink may be outlined as being “prime quality” with out being a contemporary web page, it’s simply that these are thought of the identical high quality.
To me, this backs up the significance of constantly incomes hyperlinks and explains why SEOs proceed to suggest that hyperlink constructing (in no matter type, that’s not what we’re discussing right here) wants constant sources allotted. It must be an “always-on” exercise.
5. The extra Google trusts a website’s homepage, the extra invaluable hyperlinks from that website in all probability are
We see a reference throughout the documentation (once more, within the AnchorsAnchorSource module) to an attribute referred to as homePageInfo, which means that Google may very well be tagging hyperlink sources as not trusted, partially trusted or absolutely trusted.


What this does outline is that this attribute pertains to cases when the supply web page is a web site’s homepage, with a not_homepage worth being assigned to different pages.
So, what may this imply?
It means that Google may very well be utilizing some definition of “belief” of a web site’s homepage throughout the algorithms. How? We’re undecided.
My interpretation: inner pages are more likely to inherit the homepage’s trustworthiness.
To be clear: we don’t know the way Google defines whether or not a web page is absolutely trusted, not trusted or partially trusted.
However it will make sense that inner pages inherit a homepage’s trustworthiness and that that is used, to some extent, within the weighting of hyperlinks and that hyperlinks from absolutely trusted websites are extra invaluable than these from not trusted ones.
Apparently, we’ve found that Google is storing further details about a hyperlink when it’s recognized as coming from a “newsy, prime quality” website.


Does this imply that hyperlinks from information websites (for instance, The New York Instances, The Guardian or the BBC) are extra invaluable than these from different forms of website?
We don’t know for certain.
However when taking a look at this – alongside the truth that these kinds of websites are usually probably the most authoritative and trusted publications on-line, in addition to people who would traditionally had a toolbar PageRank of 9 or 10 – it does make you suppose.
What’s for certain, although, is that leveraging digital PR as a tactic to earn hyperlinks from information publications is undoubtedly extremely invaluable. This discovering simply confirms that.
7. Hyperlinks coming from seed websites, or these hyperlinks to from these, are in all probability probably the most invaluable hyperlinks you might earn
Seed websites and hyperlink distance rating is a subject that doesn’t get talked about anyplace close to as usually because it ought to, in my view.
It’s nothing new, although. The truth is, it’s one thing that the late Invoice Slawski wrote about in 2010, 2015 and 2018.
The leaked Google documentation means that PageRank in its unique type has lengthy been deprecated and changed by PageRank-NearestSeeds, referenced by the very fact it defines this because the manufacturing PageRank worth for use. That is maybe one of many issues that the documentation is the clearest on.


In case you’re unfamiliar with seed websites, the excellent news is that it isn’t a massively complicated idea to know.
Slawski’s articles on this matter are in all probability one of the best reference level for this:
“The patent gives 2 examples [of seed sites]: The Google Listing (It was nonetheless round when the patent was first filed) and the New York Instances. We’re additionally advised: ‘Seed units should be dependable, various sufficient to cowl a variety of fields of public pursuits & nicely related to different websites. As well as, they need to have massive numbers of helpful outgoing hyperlinks to facilitate figuring out different helpful & high-quality pages, appearing as ‘hubs’ on the net.’
“Beneath the PageRank patent, rating scores are given to pages based mostly upon how far-off they may be from these seed units and based mostly upon different options of these pages.”– Invoice Slawski, PageRank Replace (2018)
8. Google might be utilizing ‘trusted sources’ to calculate whether or not a hyperlink is spammy
When wanting on the IndexingDocjoinerAnchorSpamInfo module, one which we will assume pertains to how spammy hyperlinks are processed, we see references to “trusted sources.”
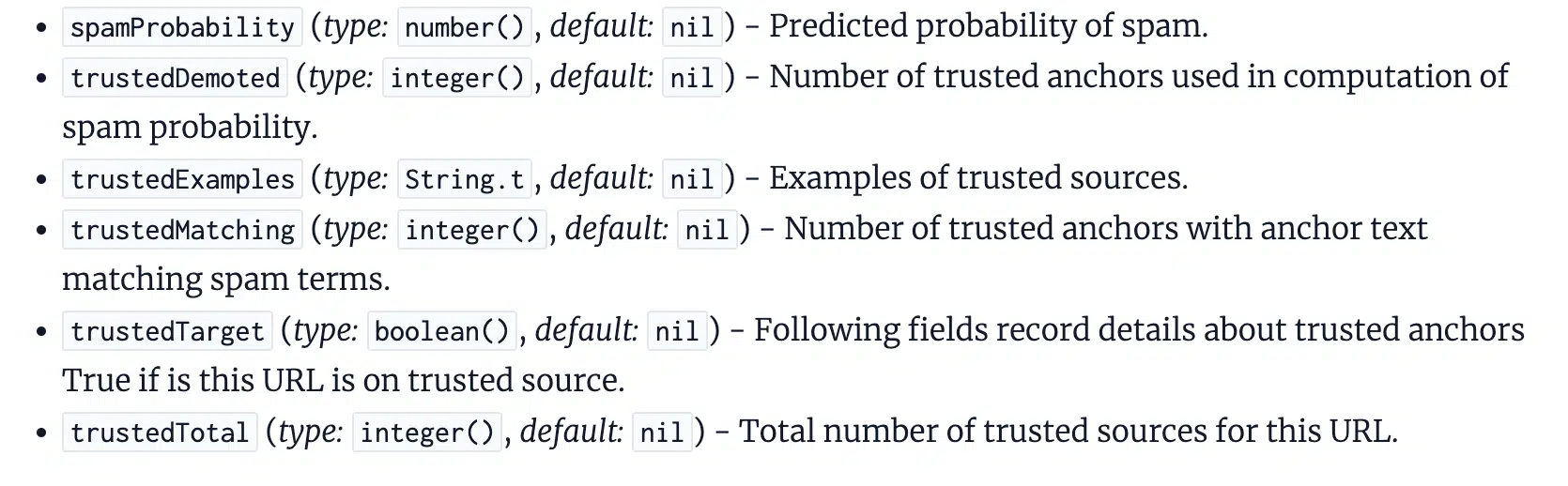

It appears like Google can calculate the chance of hyperlink spam based mostly on the variety of trusted sources linking to a web page.
We don’t know what constitutes a “trusted supply,” however when checked out holistically alongside our different findings, we will assume that this may very well be based mostly on the “homepage” belief.
Can hyperlinks from trusted sources successfully dilute spammy hyperlinks?
It’s undoubtedly attainable.
9. Google might be figuring out detrimental web optimization assaults and ignoring these hyperlinks by measuring hyperlink velocity
The web optimization group has been divided over whether or not detrimental web optimization assaults are an issue for a while. Google is adamant they’re capable of determine such assaults, whereas loads of SEOs have claimed their website was negatively impacted by this difficulty.
The documentation offers us some perception into how Google makes an attempt to determine such assaults, together with attributes that take into account:
- The timeframe over which spammy hyperlinks have been picked up.
- The common day by day fee of spam found.
- When a spike began.
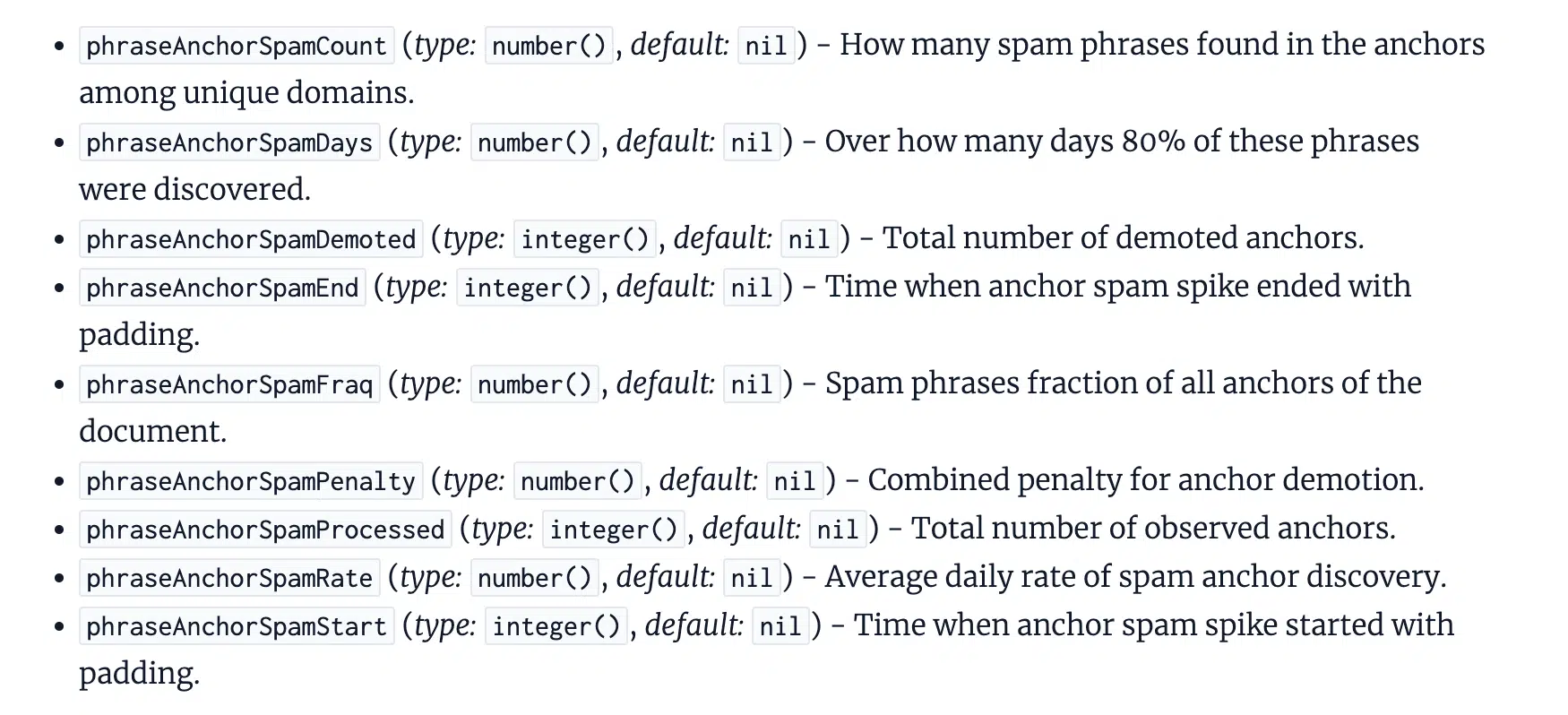

It’s attainable that this additionally considers hyperlinks supposed to control Google’s rating methods, however the reference to “the anchor spam spike” means that that is the mechanism for figuring out important volumes, one thing we all know is a standard difficulty confronted with detrimental web optimization assaults.
There are doubtless different components at play in figuring out how hyperlinks picked up throughout a spike are ignored, however we will not less than begin to piece collectively the puzzle of how Google is attempting to forestall such assaults from having a detrimental influence on websites.
10. Hyperlink-based penalties or changes can doubtless apply both to some or all the hyperlinks pointing to a web page
Plainly Google has the flexibility to use hyperlink spam penalties or ignore hyperlinks on a link-by-link or all-links foundation.


This might imply that, given a number of unconfirmed indicators, Google can outline whether or not to disregard all hyperlinks pointing to a web page or simply a few of them.
Does this imply that, in instances of extreme hyperlink spam pointing to a web page, Google can choose to disregard all hyperlinks, together with people who would typically be thought of prime quality?
We are able to’t make certain. However if so, it may imply that spammy hyperlinks should not the one ones ignored when they’re detected.
Might this negate the influence of all hyperlinks to a web page? It’s undoubtedly a risk.
11. Poisonous hyperlinks are a factor, regardless of Google saying they aren’t
Simply final month, Mueller acknowledged (once more) that poisonous hyperlinks are a made-up idea:
- “The idea of poisonous hyperlinks is made up by web optimization instruments so that you just pay them commonly.”
Within the documentation, although, we see reference given to “BadBackLinks.”


The data given right here suggests {that a} web page may be penalized for having “dangerous” backlinks.
Whereas we don’t know what type this takes or how shut that is to the poisonous hyperlink scores given by web optimization instruments, we’ve bought loads of proof to counsel that there’s not less than a boolean (usually true or false values) measure of whether or not a web page has dangerous hyperlinks pointing to it.
My guess is that this works at the side of the hyperlink spam demotions I talked about above, however we don’t know for certain.
12. The content material surrounding a hyperlink offers context alongside the anchor textual content
SEOs have lengthy leveraged the anchor textual content of hyperlinks as a approach to give contextual indicators of the goal web page, and Google’s Search Central documentation on hyperlink greatest practices confirms that “this textual content tells folks and Google one thing concerning the web page you’re linking to.”
However final week’s leaked paperwork point out that it’s not simply anchor textual content that’s used to know the context of a hyperlink. The content material surrounding the hyperlink is probably going additionally used.


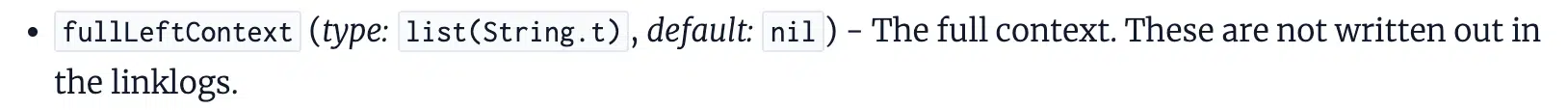


The documentation references context2, fullLeftContext, and fullRightContext, that are the phrases close to the hyperlink.
This implies that there’s greater than the anchor textual content of a hyperlink getting used to find out the relevancy of a hyperlink. On one hand, it may merely be used as a approach to take away ambiguity, however on the opposite, it may very well be contributing to the weighting.
This feeds into the final consensus that hyperlinks from inside related content material are weighted much more strongly than these inside content material that’s not.
Key learnings & takeaways for hyperlink builders and digital PRs
Do hyperlinks nonetheless matter?
I’d definitely say so.
There’s an terrible lot of proof right here to counsel that hyperlinks are nonetheless important rating indicators (regardless of us not understanding what’s and isn’t a rating sign from this leak), however that it’s not nearly hyperlinks typically.
Hyperlinks that Google rewards or doesn’t ignore usually tend to positively affect natural visibility and rankings.
Perhaps the most important takeaway from the documentation is that relevancy issues so much. It’s doubtless that Google ignores hyperlinks that don’t come from related pages, making this a precedence measure of success for hyperlink builders and digital PRs alike.
However past this, we’ve gained a deeper understanding of how Google doubtlessly values hyperlinks and the issues that may very well be weighted extra strongly than others.
Ought to these findings change the best way you method hyperlink constructing or digital PR?
That is determined by the techniques you’re utilizing.
In case you’re nonetheless utilizing outdated techniques to earn lower-quality hyperlinks, then I’d say sure.
But when your hyperlink acquisition techniques are based mostly on incomes hyperlinks with PR techniques from high-quality press publications, the primary factor is to be sure you’re pitching related tales, quite than assuming that any hyperlink from a excessive authority publication shall be rewarded.
For many people, not a lot will change. But it surely’s a concrete affirmation that the techniques we’re counting on are one of the best match, and the explanation behind why we see PR-earned hyperlinks having such a optimistic influence on natural search success.
Opinions expressed on this article are these of the visitor creator and never essentially Search Engine Land. Workers authors are listed right here.

